
The amount of data that transfers daily on a corporate network is quite important. Once a month, Windows Update has quite an impact on that amount. SCCM along Delivery Optimization can help better manage that crazy amount of GB or even TB of content required to patch all computers.
In an earlier post, we covered the topic to use with Intune and Windows Update for business
In this post, we will detail how to use SCCM Delivery Optimization to deliver Windows Updates.
Requirements
- Clients must be running Windows 10
- ConfigMgr 1910 or higher to get all
- Network ports
- 7680 inbound to allow peers
- 80 to allow computer do download updates from Windows Update
For more details, see Microsoft docs
SCCM Delivery Optimization
Using Delivery Optimization along ConfigMgr can be useful for the following reasons :
- Avoid hosting GBs of updates on-prem across many different distribution points/host/data center to support all clients download. The content also becomes obsolete about 1 month after the download and distribution date.
- Avoid using bandwidth between sites to sync GBs of updates
- Leverage local Internet access from clients to download content locally
- Self-clean up of obsolete content after a defined period.
- Still use ConfigMgr to approve updates and does not change your patch cycle strategy
- This can be leveraged for Windows 10 and Office 365 updates
Boundary Groups
Delivery Optimization, like BranchCache and Peer Cache, needs to be enabled by Boundary groups.
The Allow peer downloads in this boundary group must be checked for Delivery optimization to work.
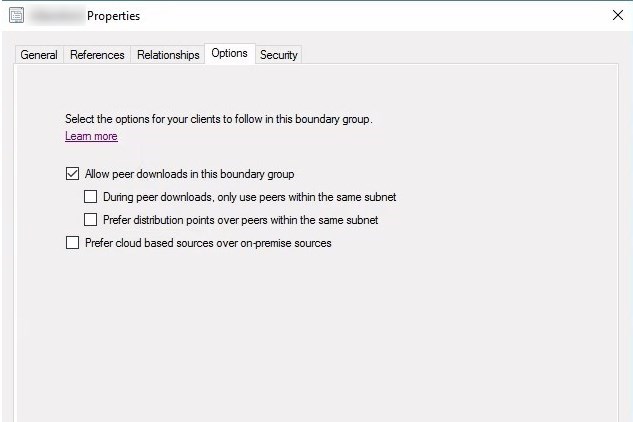
If you have large boundary groups, enabling During peer downloads, only use peers within the same subnet may be a good fit.
For more details about peer download configuration for boundary groups, see Microsoft docs.
Client settings
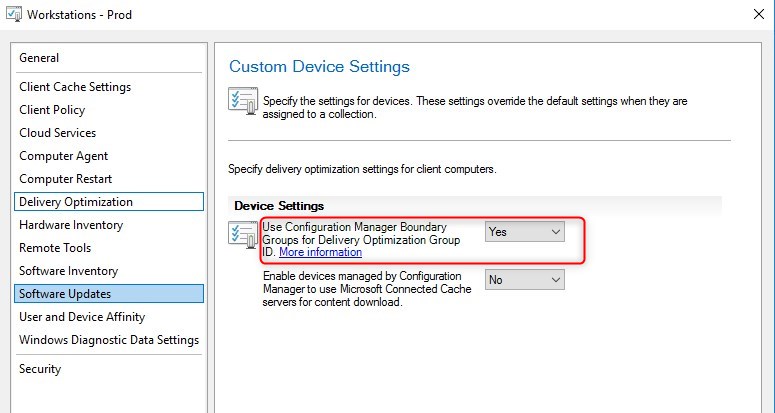
There is 2 clients settings in order for Delivery Optimization to be configured.
- Under Delivery Optimization, enable Use Configuration Manager boundary Groups for Delivery optimization for group ID
- This option will define Delivery Optimization in Group Mode, which was pretty hard to achieve without boundary groups.
- Under Software Update, enable Allow Clients to download delta content when available.
- This does NOT require to enable Express Update on your Software Update Point.
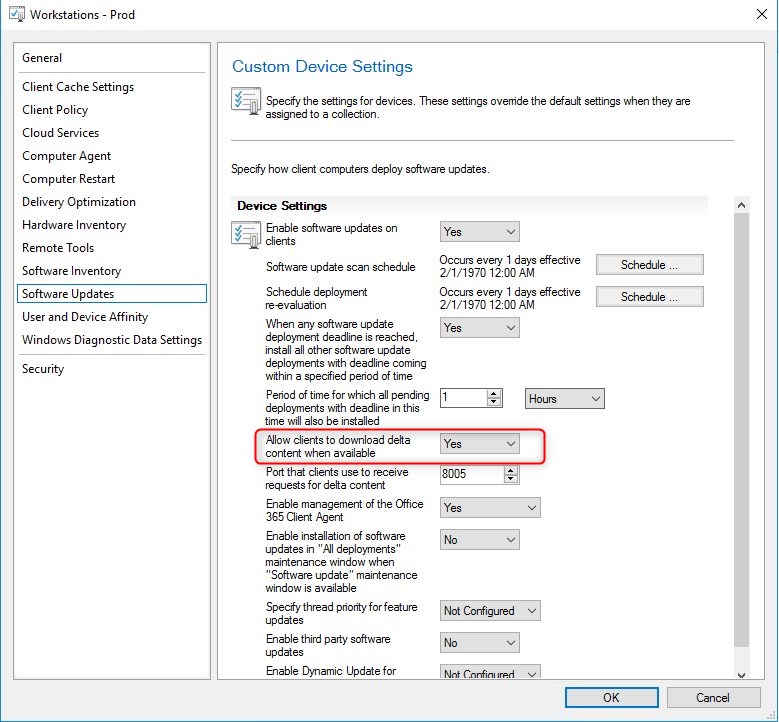
- Those client settings will create the following local policies on Windows 10 devices.
Delivery Optimization’s GPO
Why are GPO required on top of the ConfigMgr client configuration? Because some default values are a bit low to see a real benefit from using Delivery Optimization
The following GPO should be review and changed to recommended value.
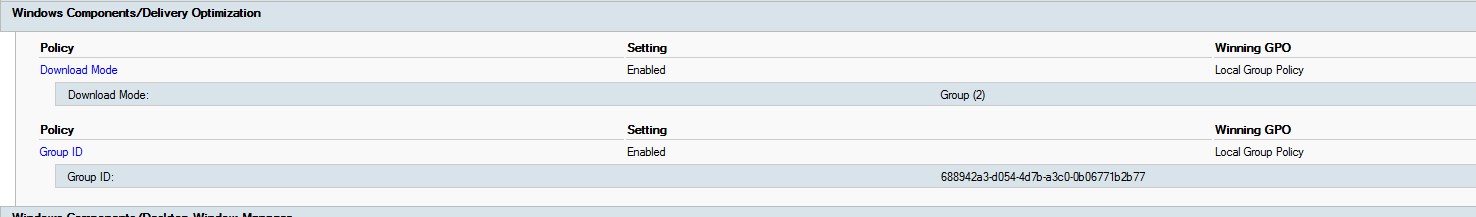
- Under Computer Configuration/Administrative Templates/Windows Component/Delivery Optimization, enable Max Cache Age
- By default, it is set to 3 days, which is a bit fast to allow computers to share over your patching cycle
- 1814400 seconds is 30 days wish is reasonable to expire content prior to next cycle.
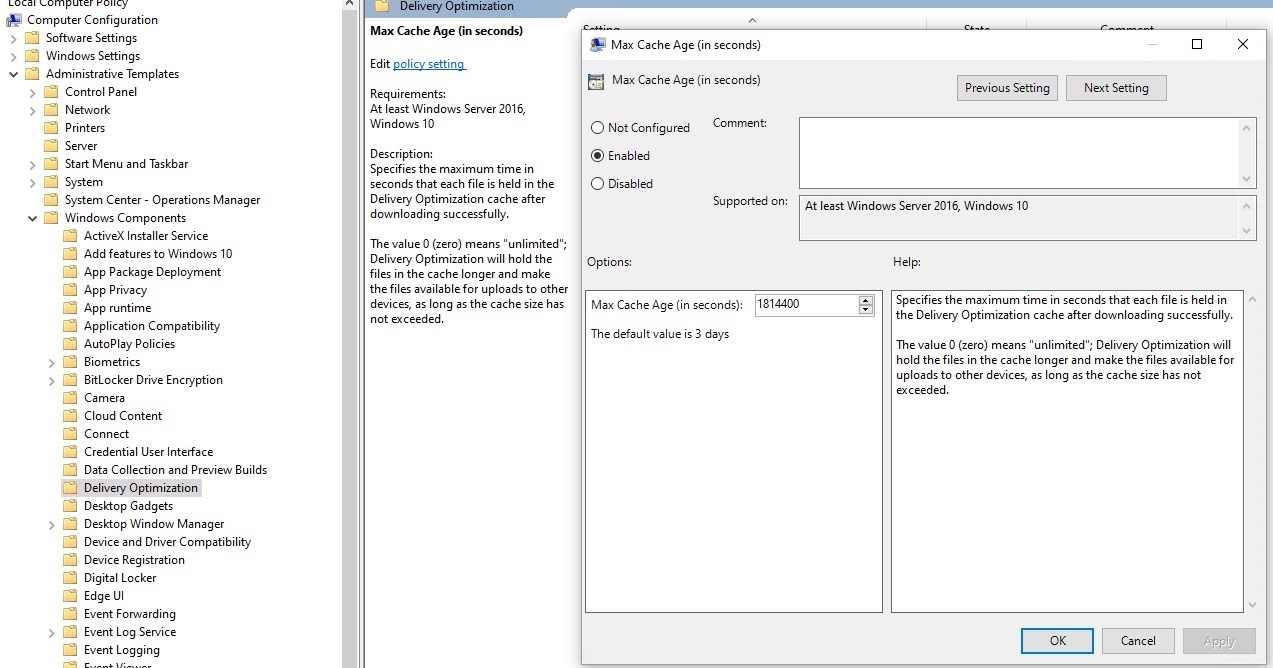
- Under Computer Configuration/Administrative Templates/Windows Component/Delivery Optimization, enable Minimum Peer Caching Content file size
- By default, it is set to 100mb. This isn’t critical for Windows Updates but could become really useful to allow computers to share content for smaller content, like Windows store apps that about for about 100MB per client per month.
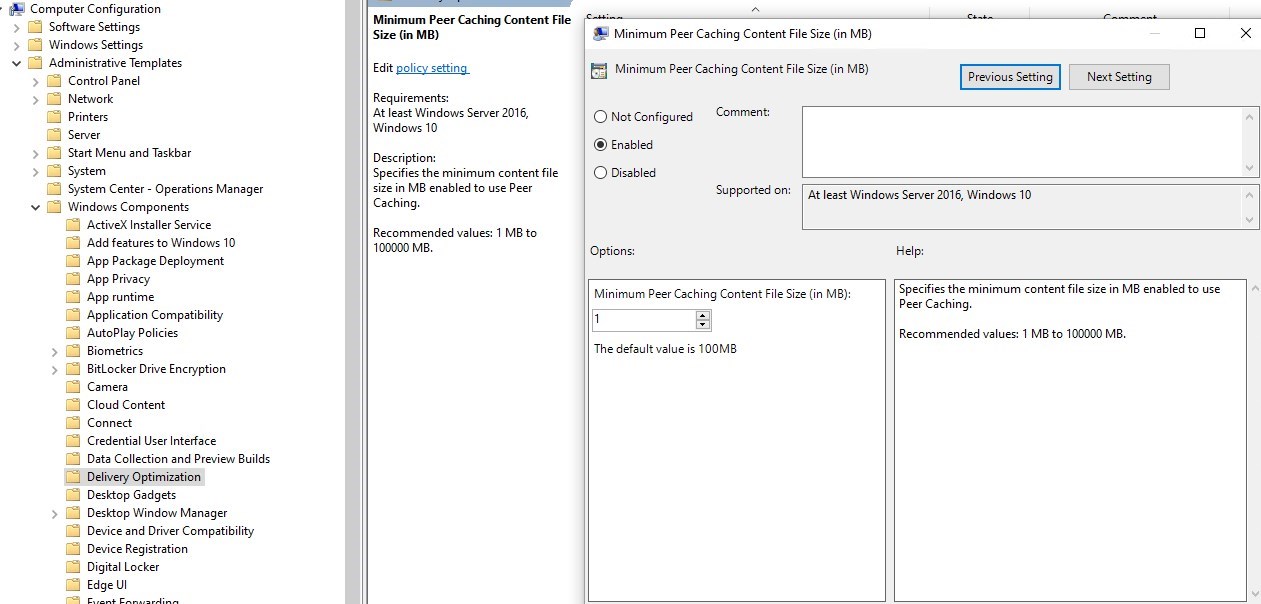
- Under Computer Configuration/Administrative Templates/Windows Component/Delivery Optimization, enable Delay Foreground download from HTTP
- By default, it is set to 0 seconds, so it doesn’t allow computers to reach for content on Peers. Again not mandatory in terms of monthly patching from ConfigMgr, but useful for Microsoft store apps updates.
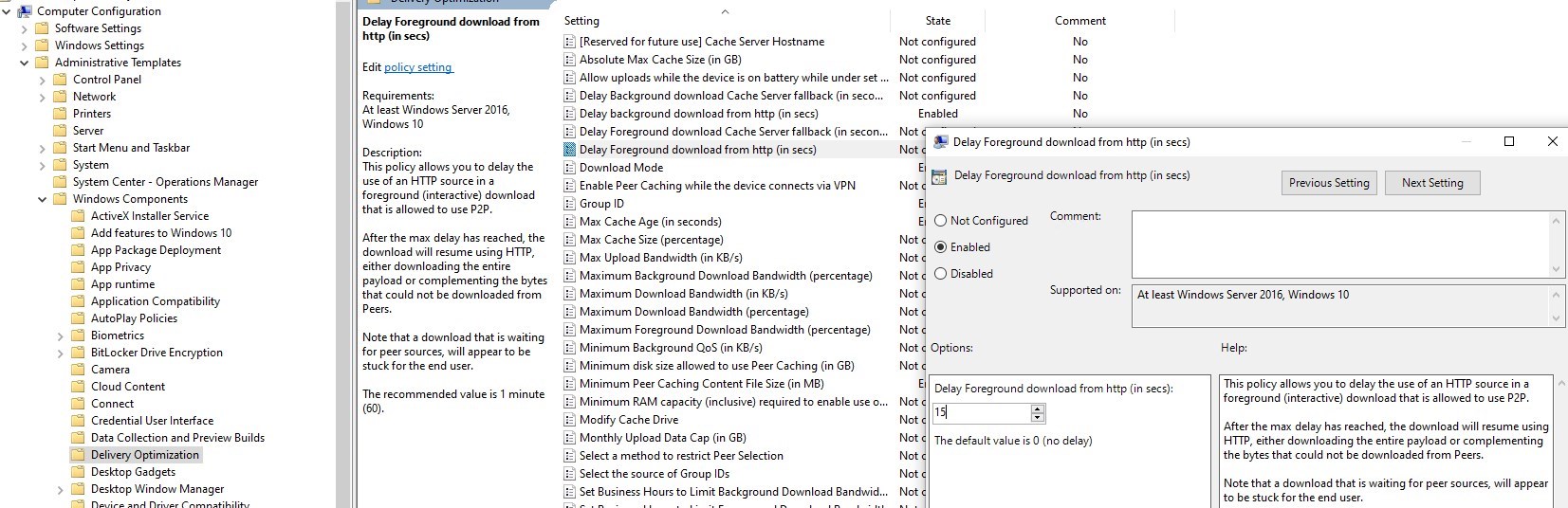
- Under Computer Configuration/Administrative Templates/Windows Component/Delivery Optimization, enable Delay background download from HTTP By default, it is set to 0 seconds, so it doesn’t allow computers to reach for content on Peers. We decided to wait for 60 seconds prior to reach online for content. This is mostly for clients that are past due the schedule and haven’t downloaded to content ahead. It could generate large delay in user experience.
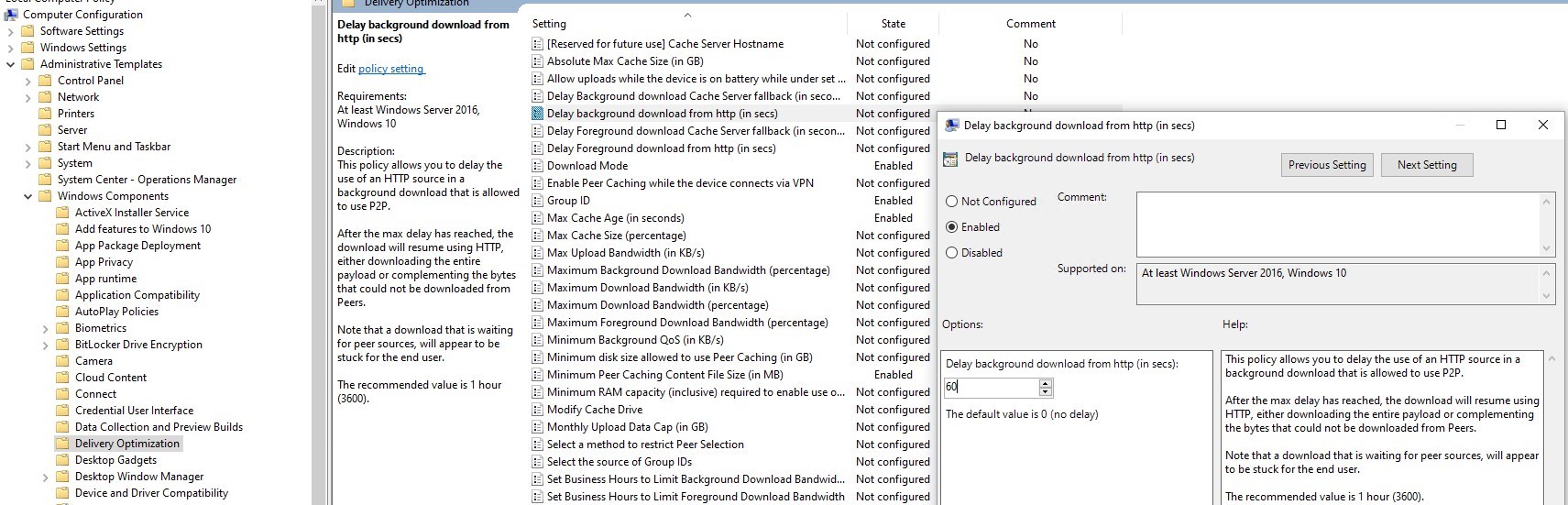
For more details about Delivery Optimization configuration, see Microsoft Docs
Software Update deployment
In order to make to most out of Delivery Optimization, clients must get updates from Microsoft Update, otherwise, other services like BranchCache will take over if downloaded from an internal source.
- To allow clients to get updates from Windows Update, check the box If software updates are not available on Distribution point, download content from Microsoft Update. This is done on the deployment of the Software Update group.
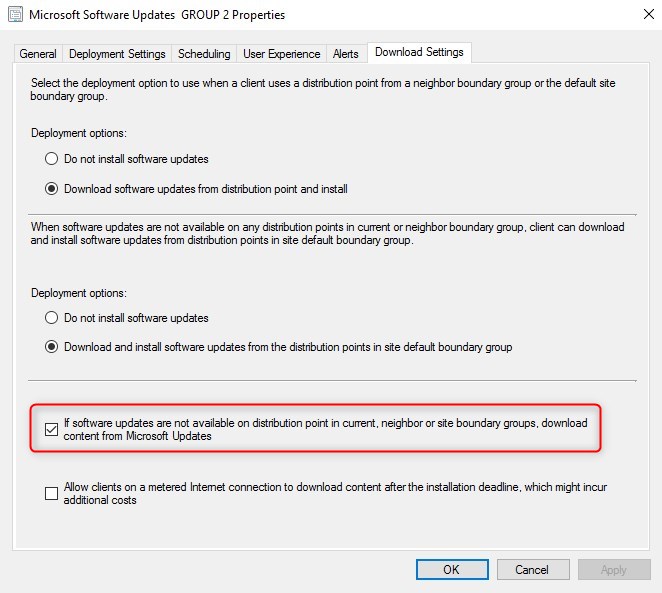
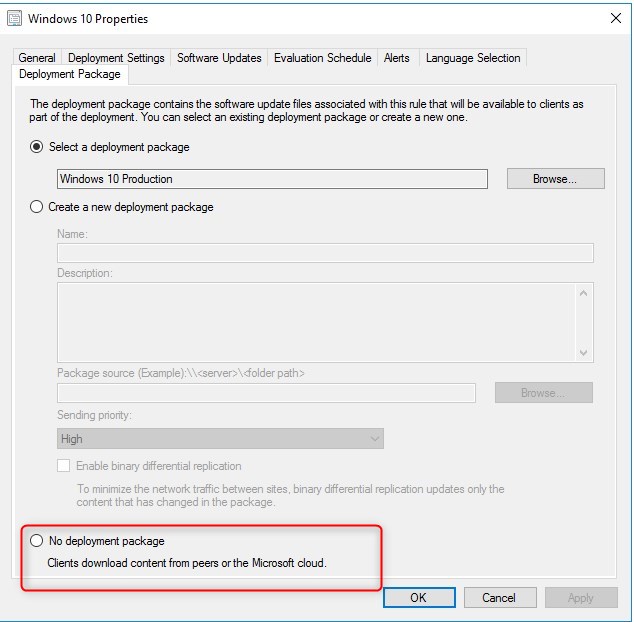
- That checkbox alone isn’t enough. If updates are available on a local Distribution Point, it will ignore any DO configuration and download locally. The Distribution point for the client must not host Windows update files.
- This means remove the Software Update Package from the distribution point
- Eventually, even the Automatic deployment rule can be modified to not even attempt to download updates if 100% of your clients gets content from Microsoft Update
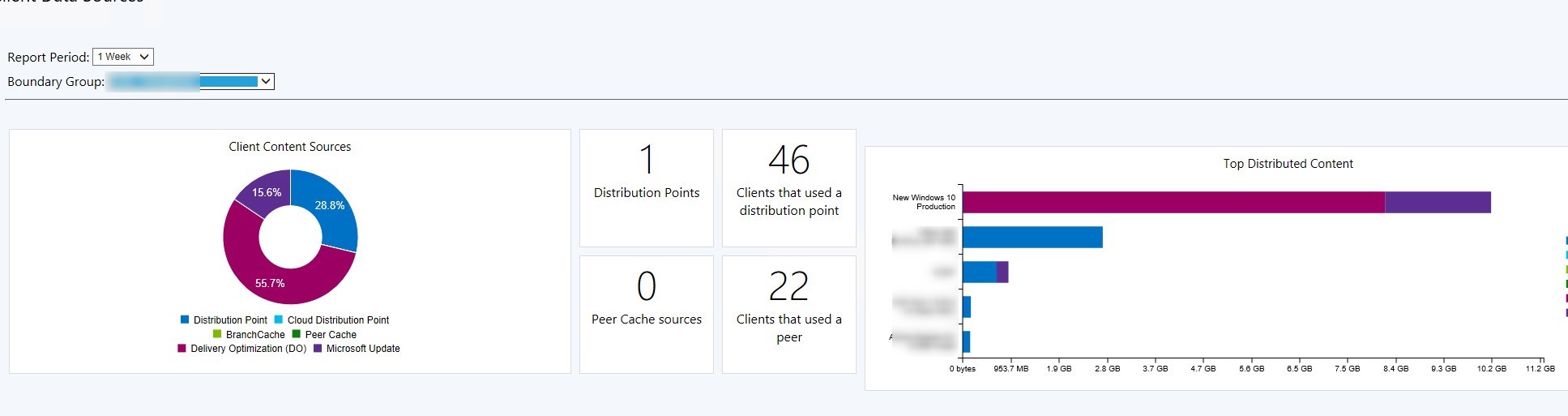
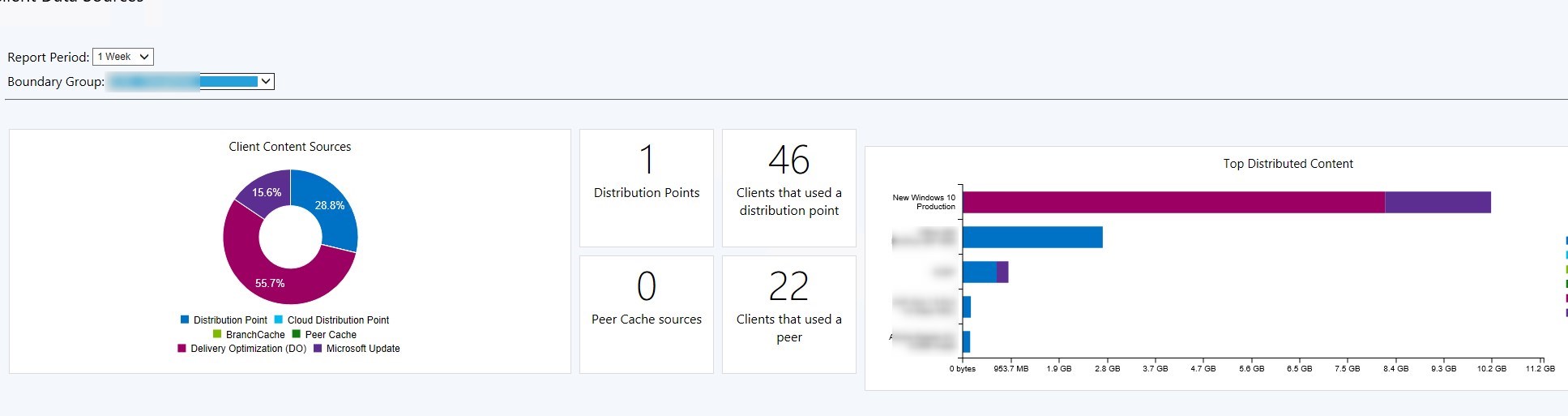
Delivery optimization Results
The following month of patching will reflect the gain of using Delivery Optimization. To review it, browse to Monitoring / Distribution Status / Client Data source
Locally on clients, there’s a few Delivery optimization cmdlet to review usage.
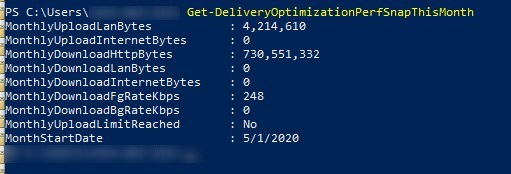
Get-DeliveryOptimizationPerfSnapThisMonth
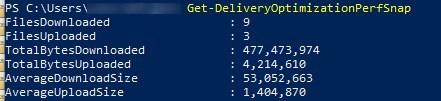
Get-DeliveryOptimizationPerfSnap
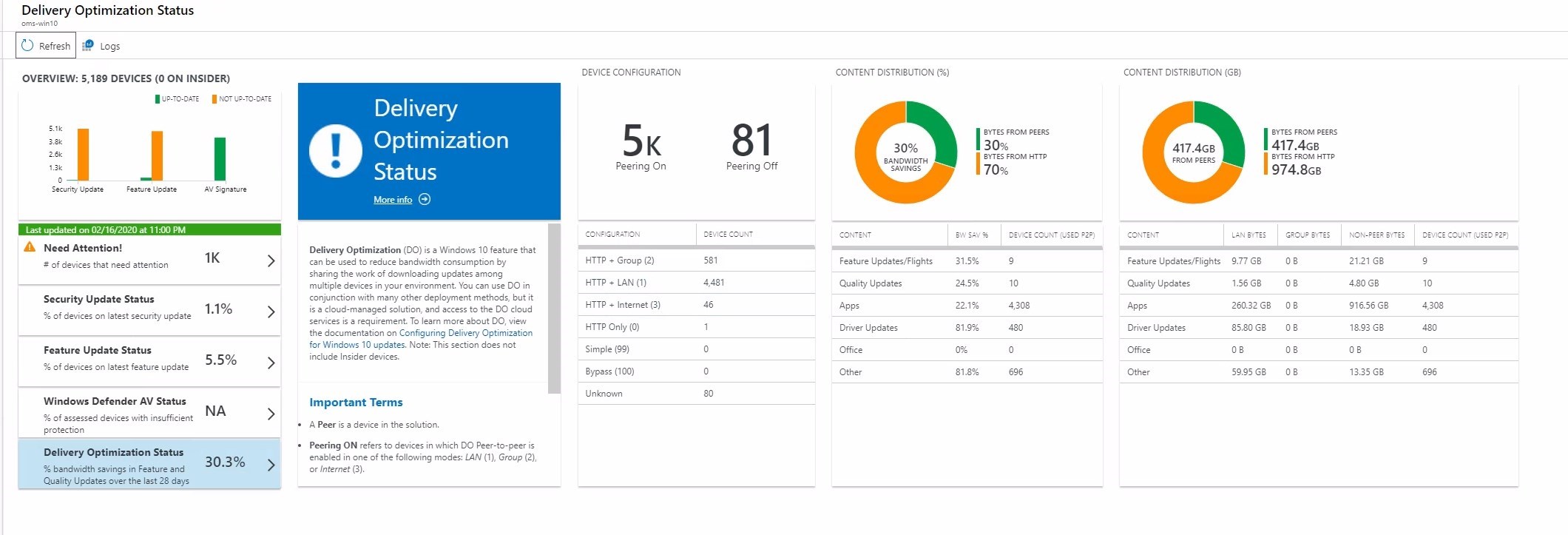
A side benefit of using Delivery Optimization
As explained earlier, leveraging Delivery Optimization for ConfigMgr content can also be useful for Apps updates from the Windows Store. Windows 10 computers download about 100mb worth of updates for all apps per month. Multiply this by the number of devices you have, and a TB of content will quickly arrive.
The below screen is taken from Update compliance that tracks this information, while ConfigMgr only reports content from Windows Updates.
Bonus Resources
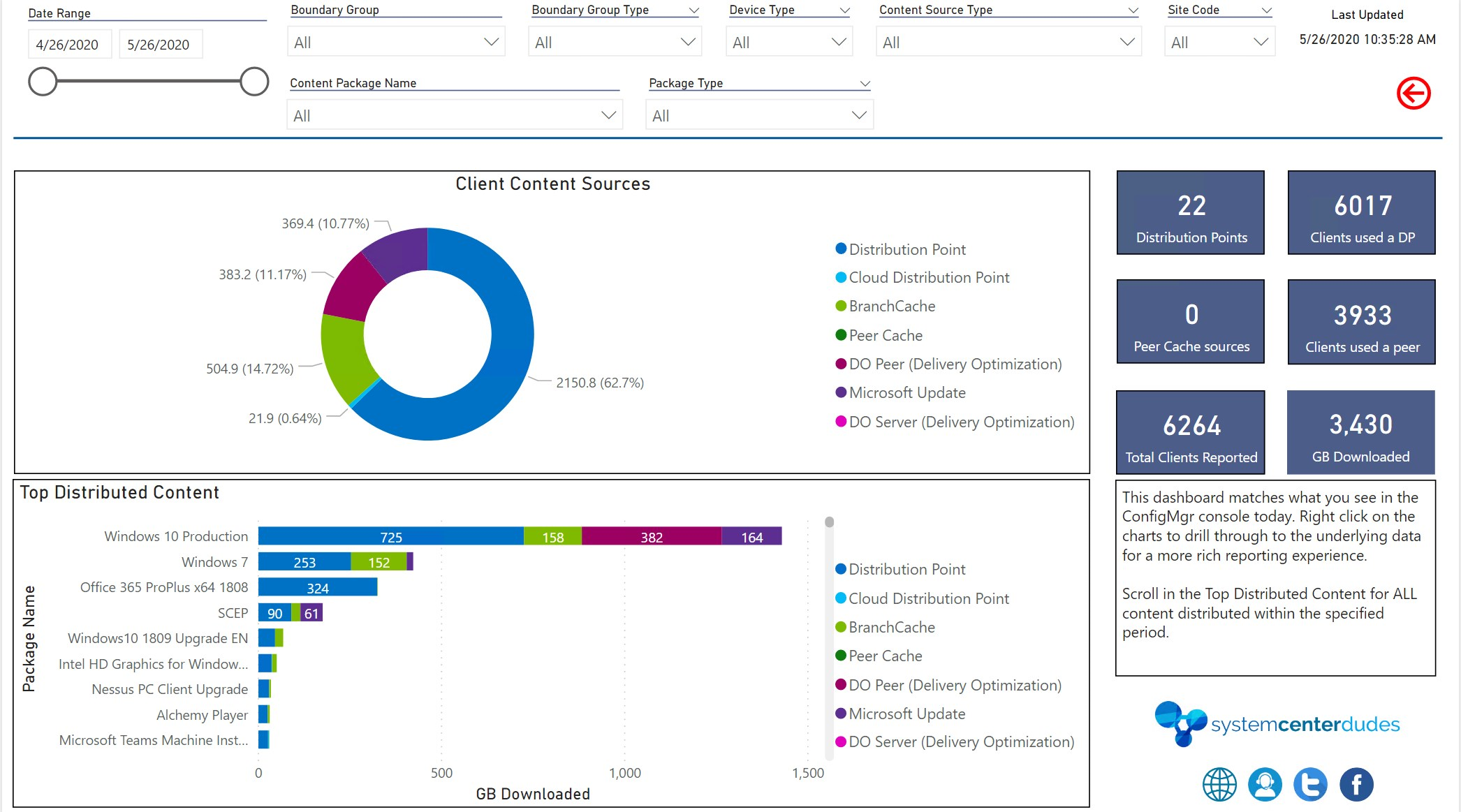
Are you using Power BI? We did an insane report regarding client content usage. You will have a better idea of which client is using which type of content.
Bottom notes
- Be patient to see results
- There’s also Microsoft Connected Cache, AKA Delivery Optimization In-Network Cache(DOINC), available if you wish to configure your distribution point as DO caches.
For more on ConfigMgr Delivery Optimization, see Microsoft docs.
Hope this helped!












Mario Ferrante
12.11.2020 AT 06:48 AMJonathan Lefebvre
12.11.2020 AT 08:35 AMcapnjax21
12.11.2020 AT 11:43 AMJonathan Lefebvre
12.14.2020 AT 12:24 PMcssh
09.01.2020 AT 03:19 PM