
It’s been over a year since our initial post about enabling Co-Management. Several improvements have been made so it’s worth revisiting the Co-Management SCCM 1902 topic.
Co-Management SCCM 1902 Prerequisites
- Azure Subscription
- Azure Active Directory Premium
- Microsoft Intune subscription OR Enterprise Mobility + Security (EMS) subscription
- Client computer using Hybrid Azure AD Joined (domain + AAD joined) using Azure AD Connect.
Enable SCCM 1902 Co-Management
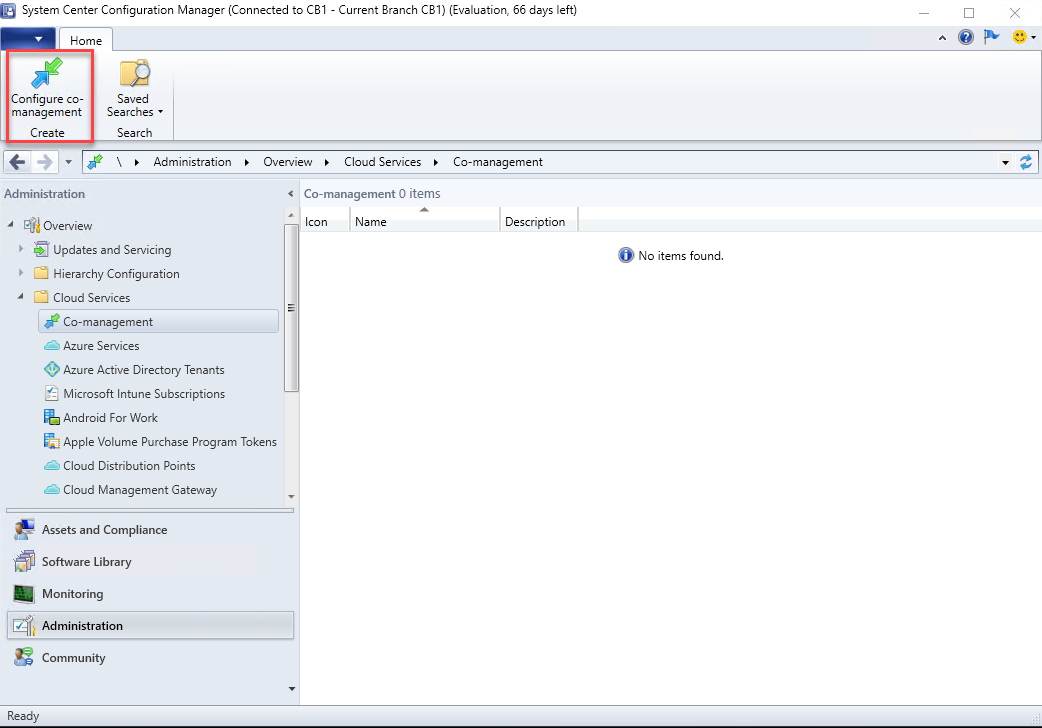
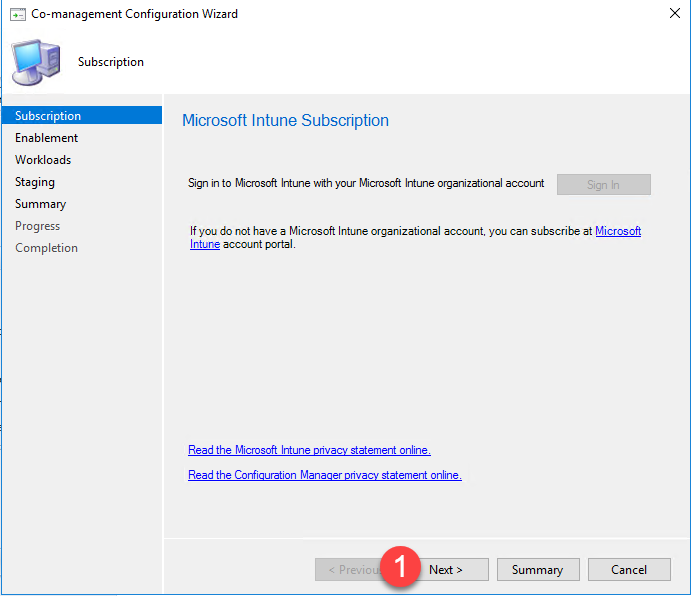
- Navigate to Administration / Cloud Services / Co-Management and select Configure Co-Management
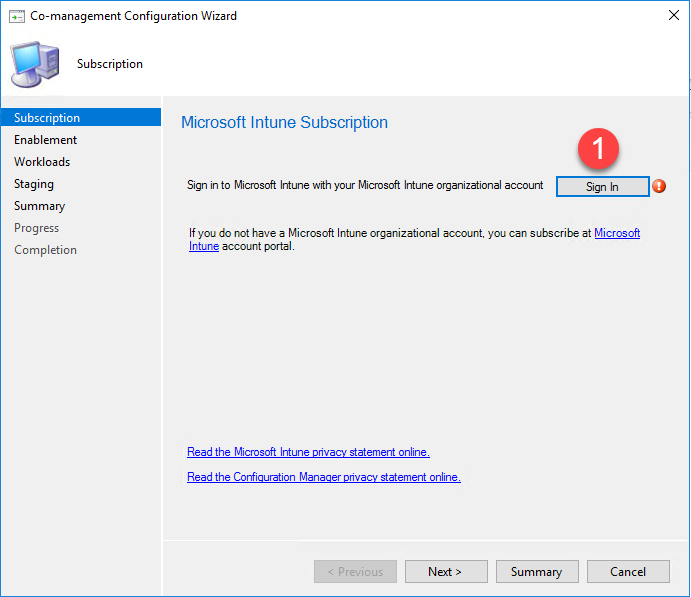
- Click Sign In to enter your Intune credentials.
- After signing in, click Next.
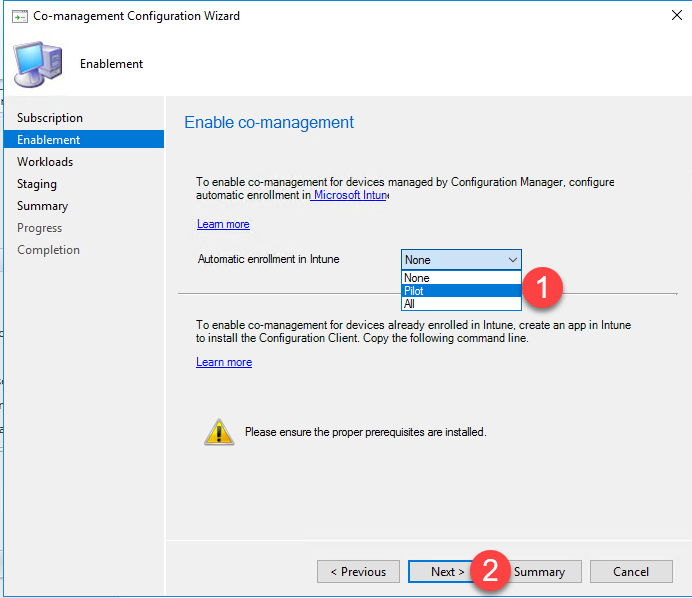
- Configure Automatic enrollment in Intune. Select None or Pilot at this time. You can change this setting later. You can select your pilot collection later.
- Select Pilot then click Next.
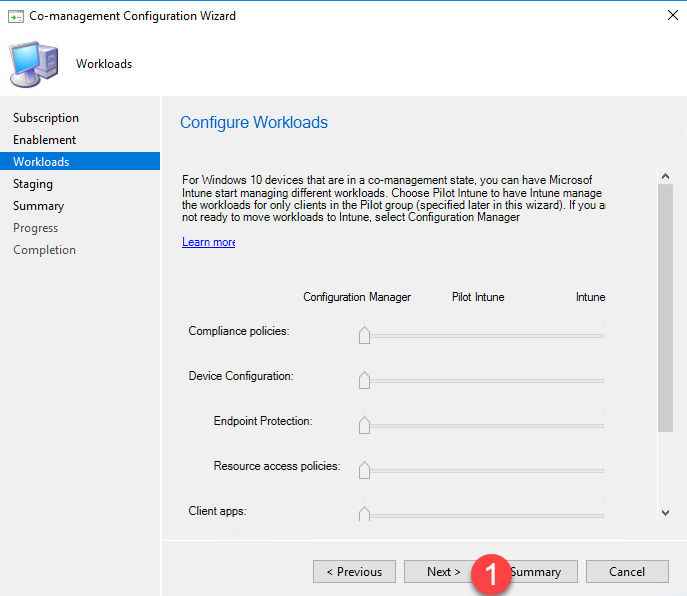
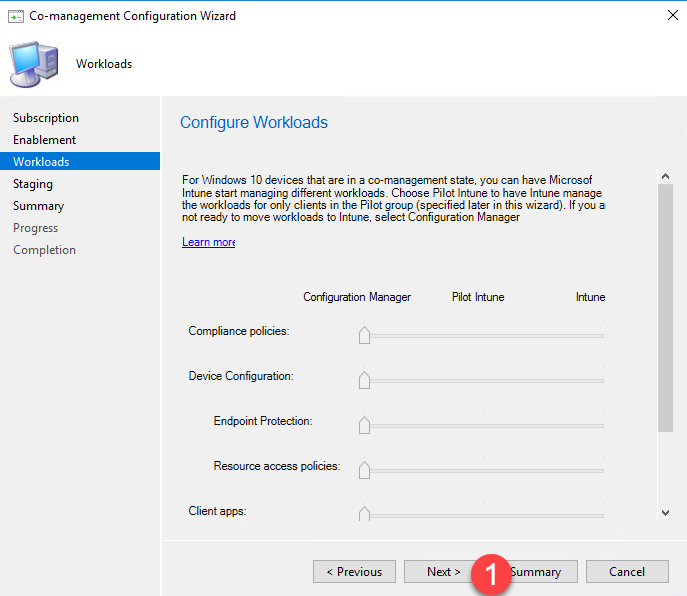
- Configure Workloads lets you choose which workloads will be managed by which system – Configuration Manager or Intune. Don’t change any settings at this time and click Next.
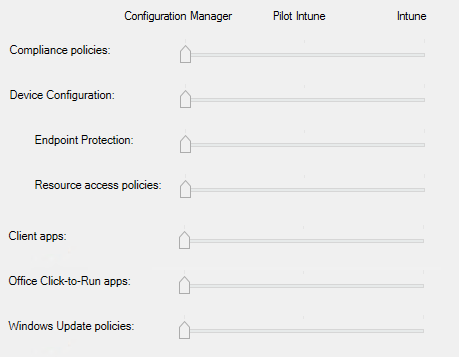
- Full list of workloads from the wizard:
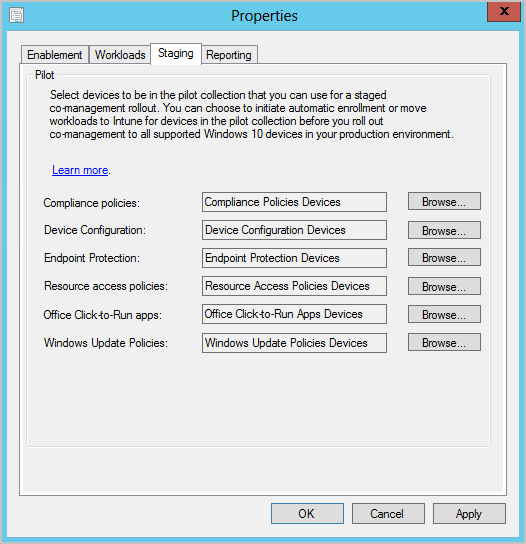
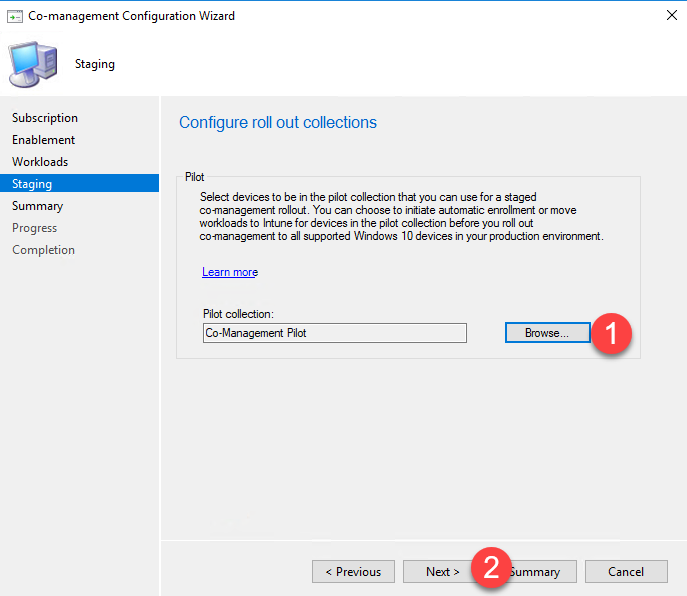
- Configure the roll-out collections allows you to select the collection to use for deploying Co-Management. In this example, we selected our Co-Management Piloting collection.
- Click Next.
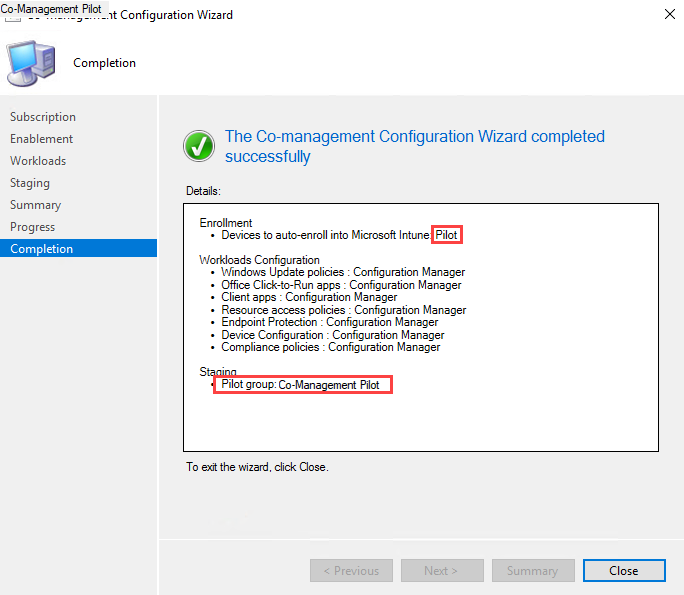
- On the summary screen, click Close.
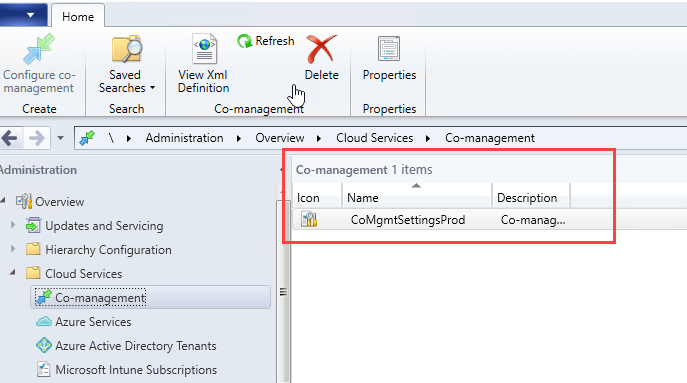
- Back in the console, verify that Co-Management appears. This is where you go to configure Co-Management workloads and targeted collections.
Enroll Windows 10 1903 Client Into Intune for Co-Management
Client Settings
The Client Cloud Services node in the client settings policy allows you to configure devices to automatically register in Azure Active Directory instead of using a GPO as was previously necessary.
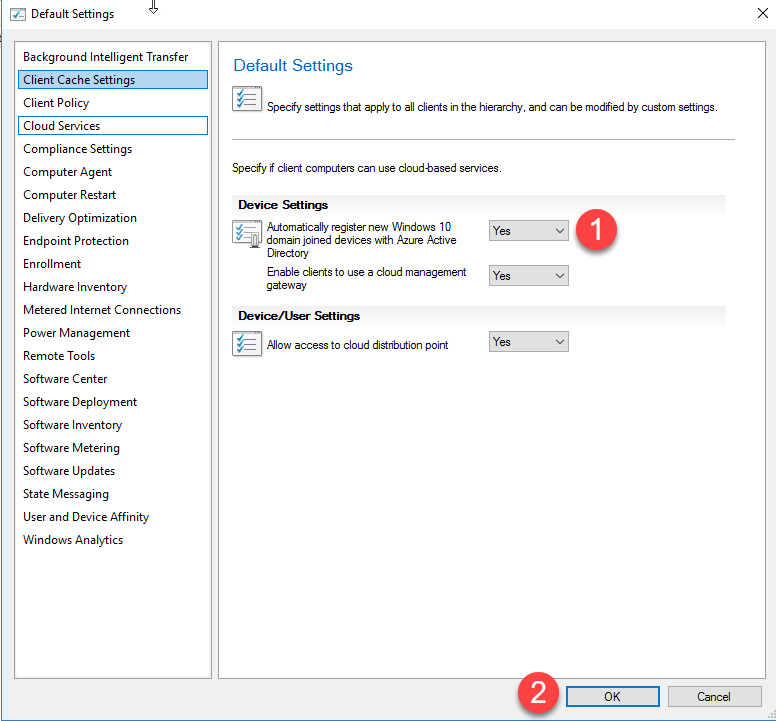
- Open a Client Settings policy and select Cloud Services.
- Set Automatically register new Windows 10 domain joined devices with Azure Active Directory to Yes then Click OK.
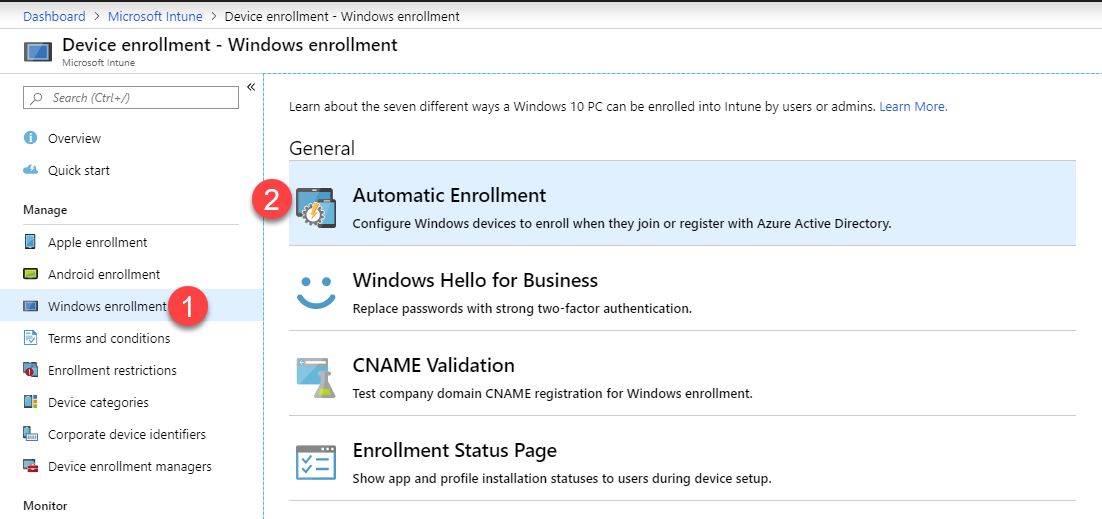
Intune Auto Enrollment
- In your Intune tenant, navigate to Device Enrollment > Windows Enrollment.
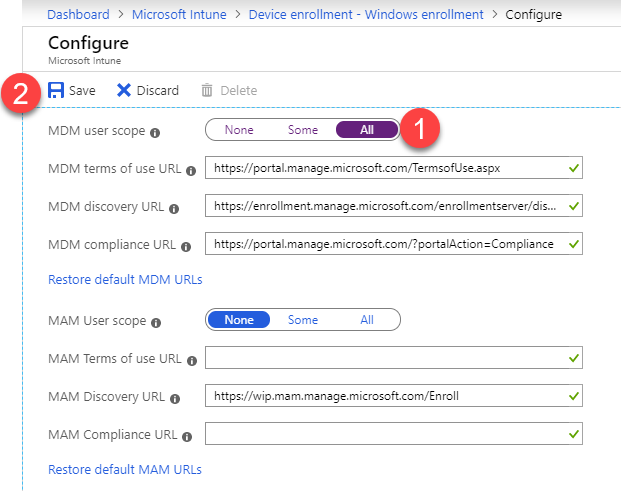
- Change MDM user scope to Some or All – if you choose Some, you will have to specify an AAD User Group.
- * NOTE* – If you enable MDM and MAM for the same group, only MAM is enabled for those users and they will not auto enroll in Intune.
Assigning Licenses
You must also be sure to assign an Intune license to any user who will use a co-managed device.
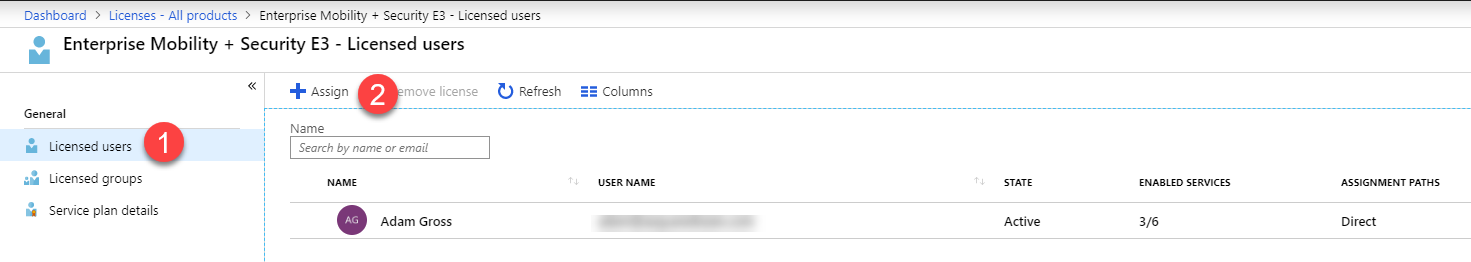
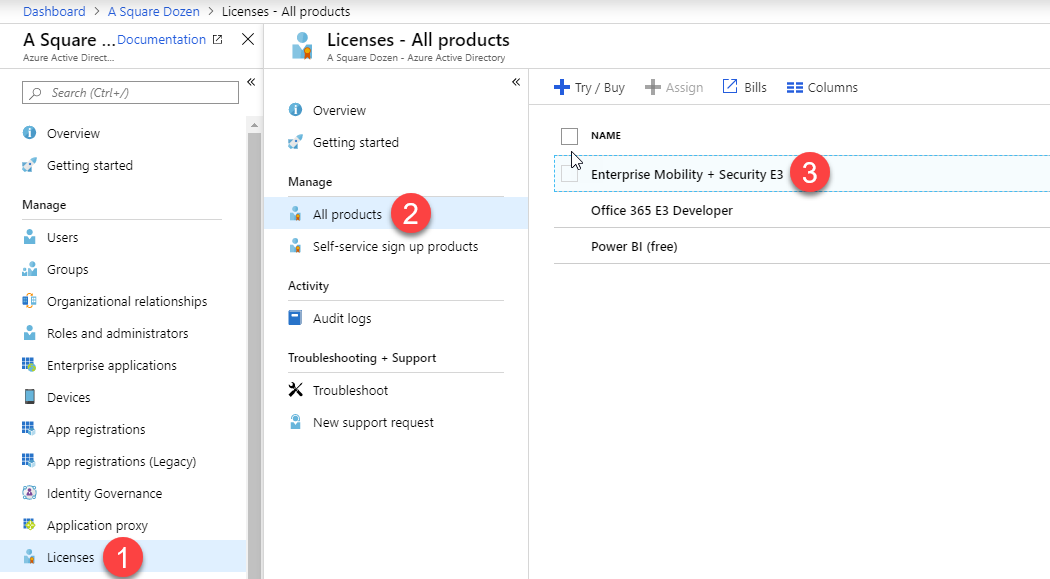
- Navigate to Azure Active Directory > Licenses > All Products
- Select the product with Intune licenses – in this case, Enterprise Mobility + Security E3.
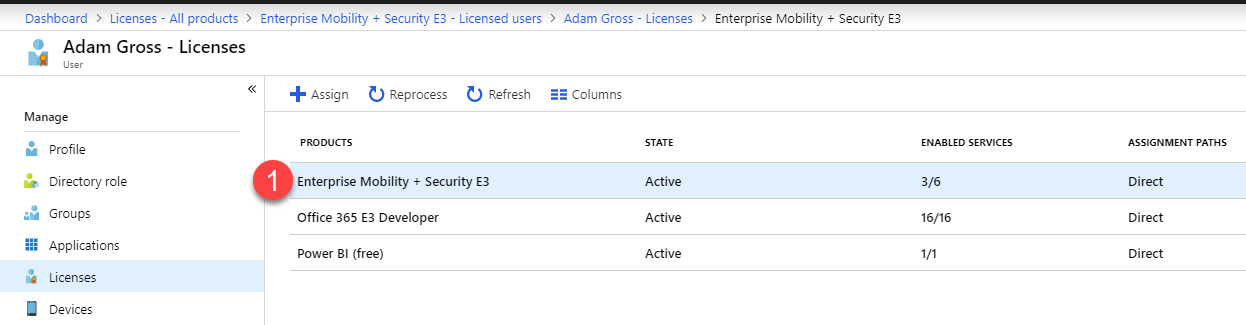
- Select Licensed users or Licensed groups then select Assign to select a user or group to assign to.
- Select the License you want to assign
- Click Configure required settings then select the product license you want to assign then click Select.
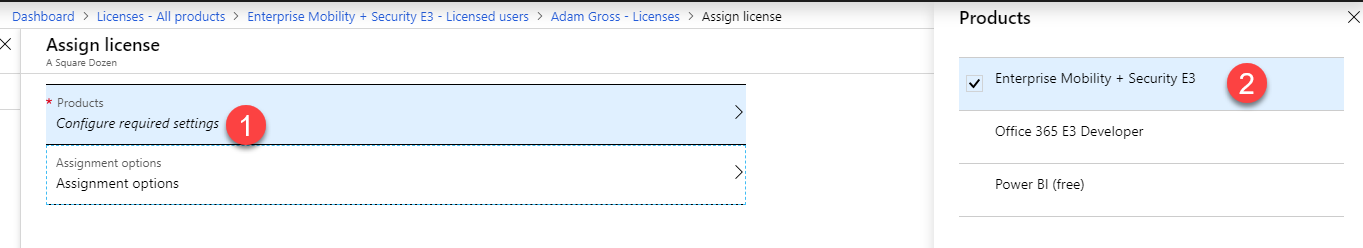
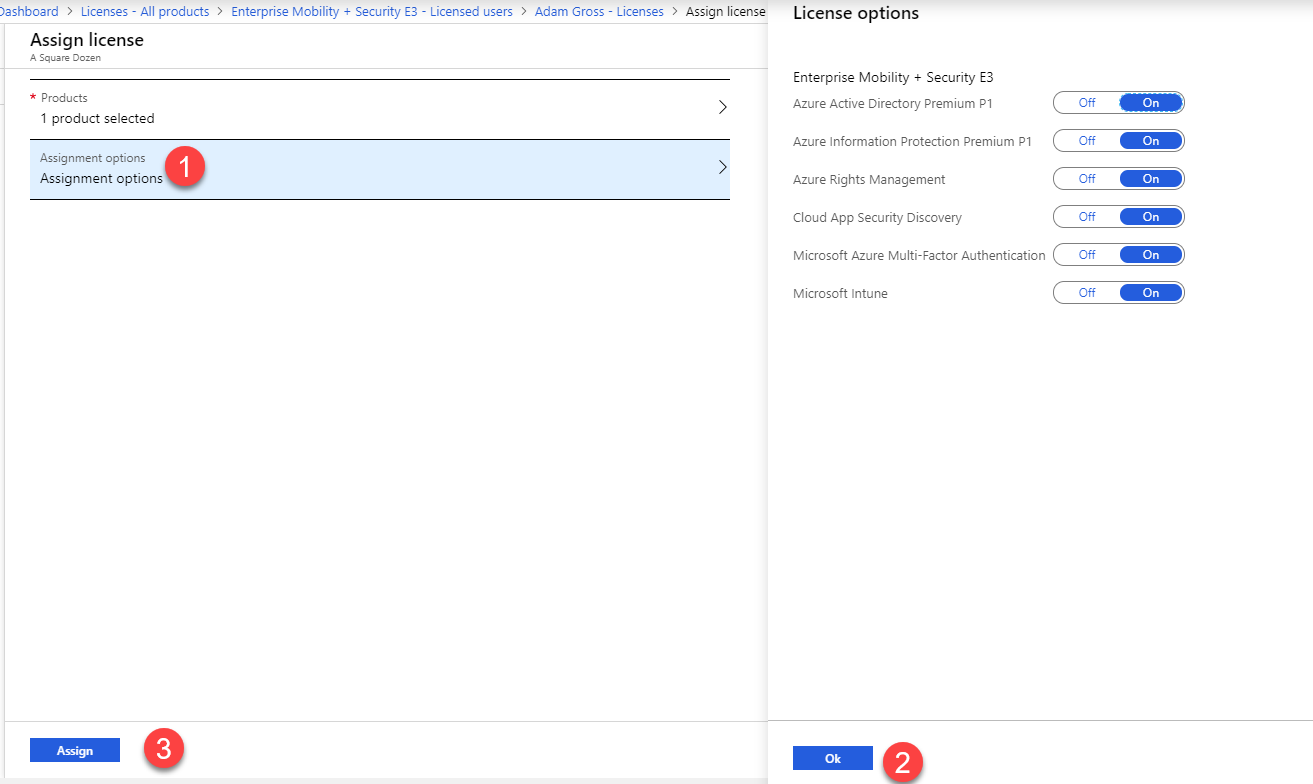
- Click Assignment Options
- Make any needed change to License options and click OK then click Assign.
Auto-Enrollment Verification
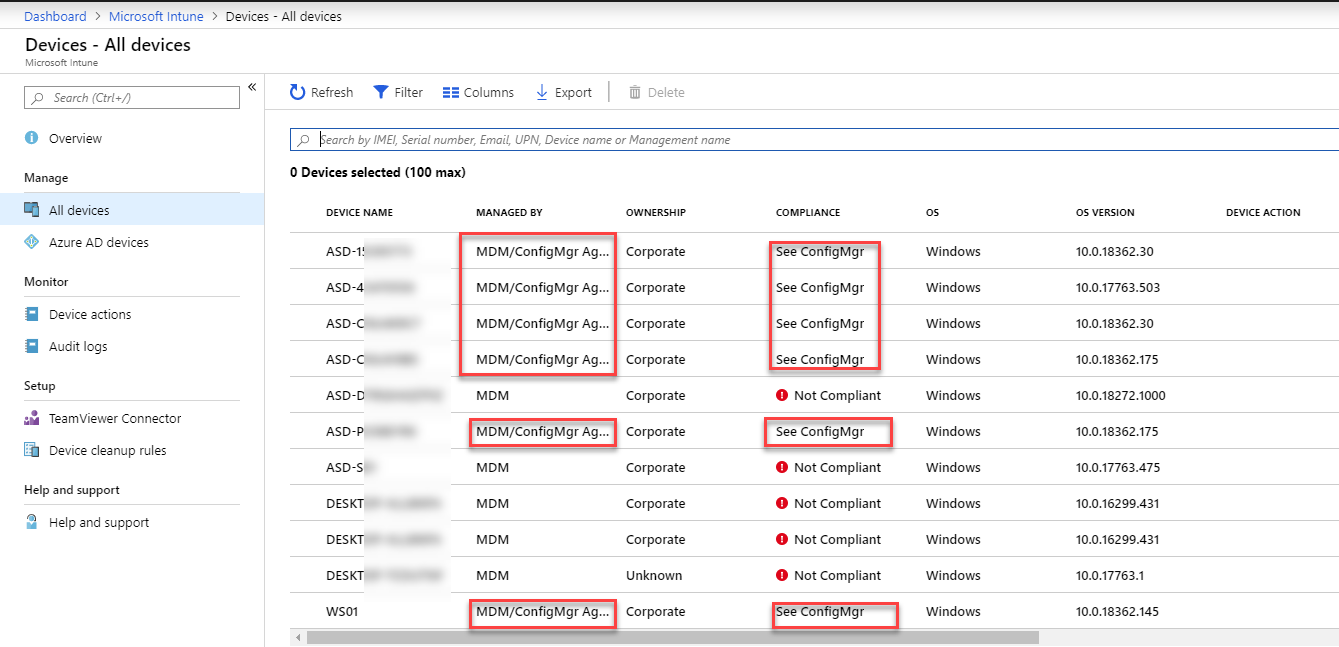
To verify that devices are being auto-enrolled and managed by SCCM, you can review the Devices node in Intune. the Managed By and Compliance columns will indicate whether they are managed by ConfigMgr or not.
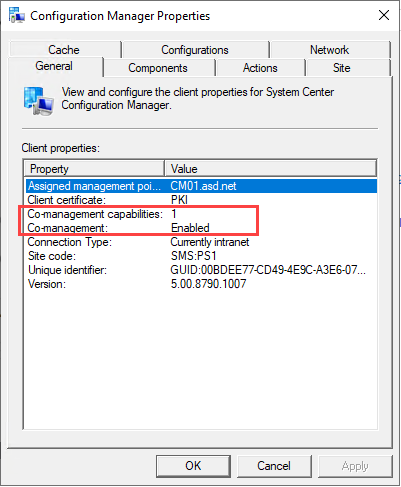
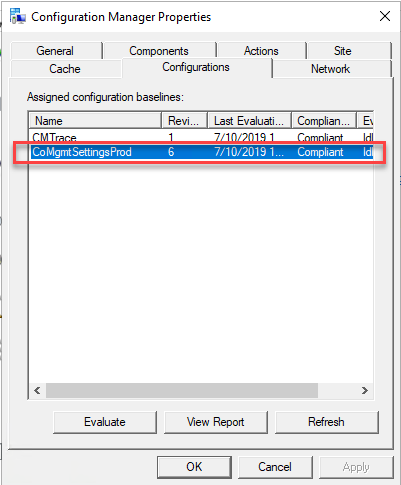
On a Windows device, you can also check the SCCM compliance settings to ensure verify Co-Management compliance and also see the number of workloads are managed by via Co-Management.
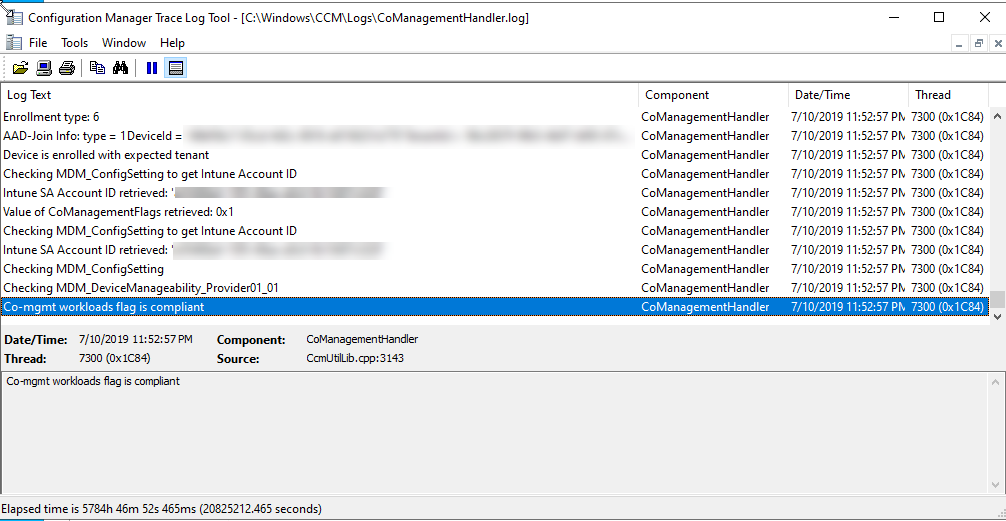
You can also review CoManagementHandler.log in the CCM Logs folder on the client to see Co-Management related client logs.
Moving Workloads to Intune
As I’m writing this, David James just tweeted that SCCM 1906 will likely ship in a few days. Based on past Technical Preview releases, I’m expecting to multiple pilot groups for Co-Management added on 1906. I will write a new post on moving workloads to Intune in 1906 to include the new options in that post.












BigIve
09.17.2020 AT 08:18 PMJim
04.23.2020 AT 07:47 AMJim
04.23.2020 AT 07:46 AMTony
04.22.2020 AT 12:35 PMGwyn
01.29.2020 AT 09:38 AMKeith
12.03.2019 AT 10:35 AMChris
01.17.2020 AT 03:30 AMJames
08.15.2019 AT 04:52 PMMatt Robertson
07.19.2019 AT 10:10 AMAdam Gross
07.19.2019 AT 10:25 AMMatt
07.18.2019 AT 08:45 AM