
The majority of companies use SCCM to manage laptops, computers, servers and some for mobile devices, if they use Microsoft Intune in hybrid mode. In some situations, Intune and SCCM management is done by 2 different teams. Except for the Full Administrator role in SCCM, it’s possible to separate Intune with Configuration Manager infrastructure in the console by using security roles and security groups (RBAC).
The goal is to ensure that an Intune administrator does not access Configuration Manager client devices and objects, as you don’t want to end up with people who may wipes or manages mobile devices when they are supposed to be only Configuration Manager admins.
This post will explain how to strengthen security and separate Intune with Configuration Manager infrastructure in SCCM console.
Create Devices Collection for Intune Client
The first thing to do is create a device collection that targets Intune clients. There’s two ways to create a device collection, manually or automatically. A set of operational SCCM collections by MVP Benoit Lecours is available to install where you can use the Mobile Devices | All collection as your Intune clients device collection. If it’s the case, move to the next section, otherwise create the devices collection manually:
- Open the SCCM console and navigate to Assets and Compliance / Device Collections
- Right-click on Device Collections and select Create Device Collection
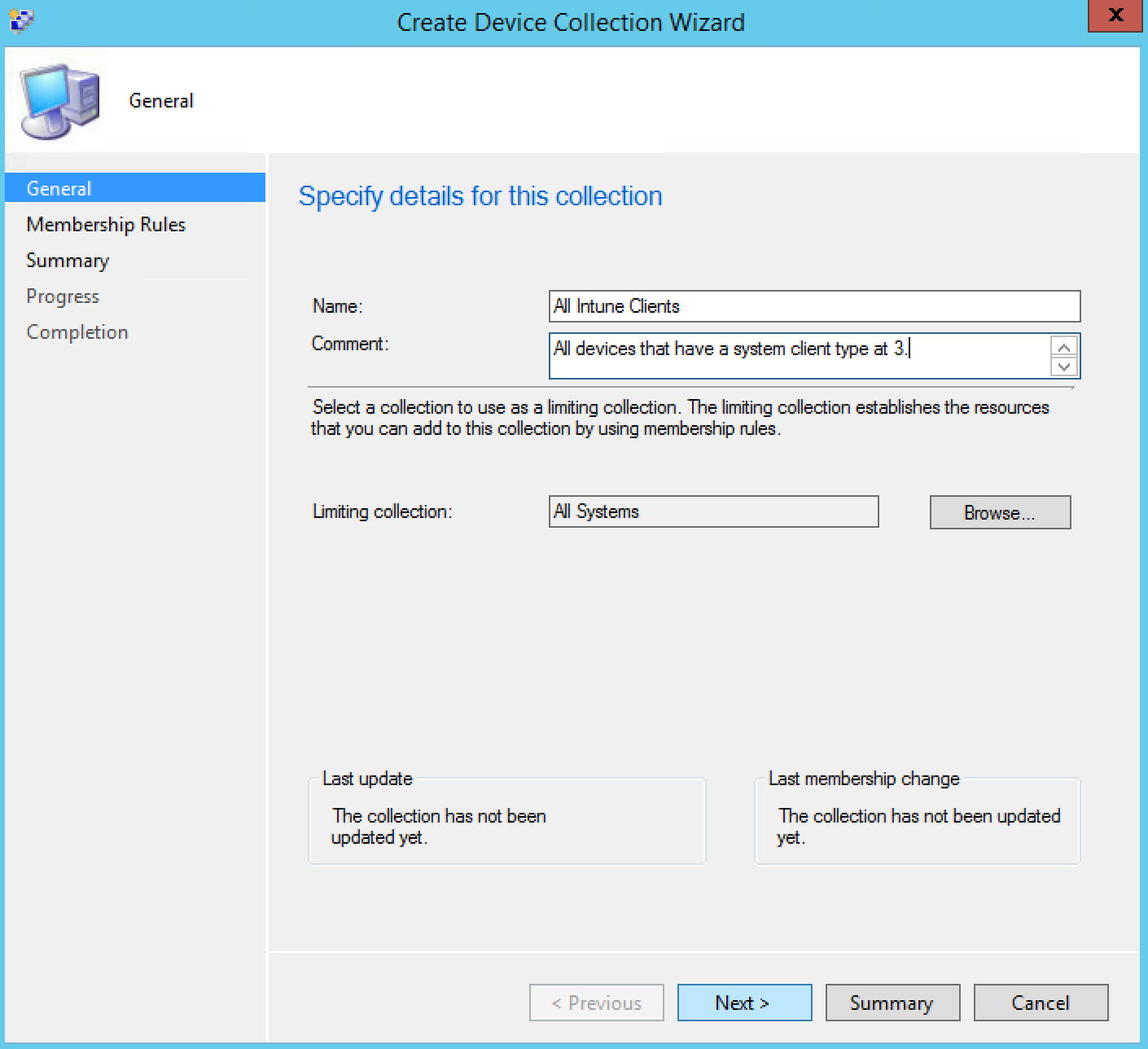
- From the General tab, enter a name for your collection and also limit the collection membership to All Systems, once you’re finish, click Next
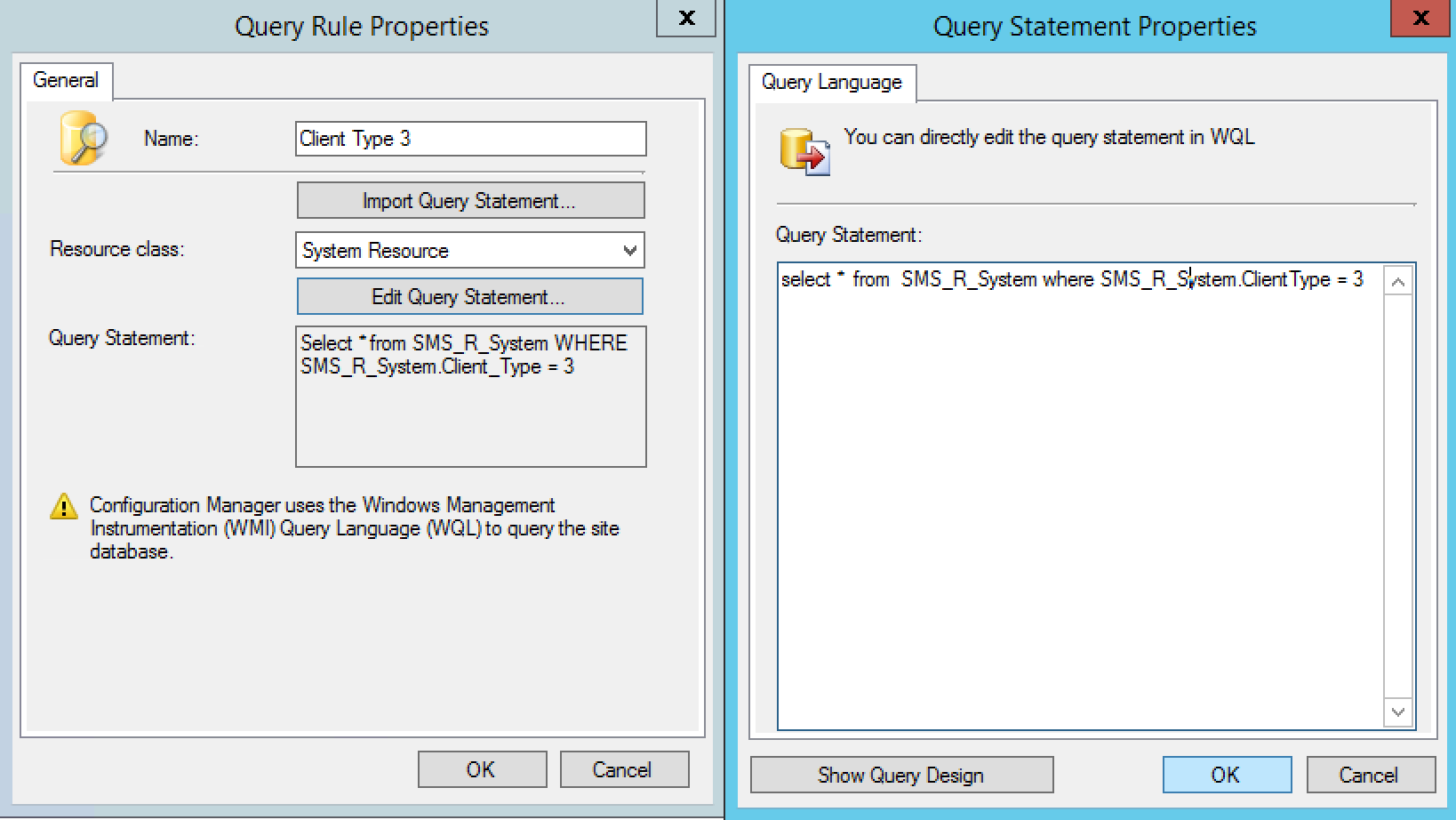
- In the Query Rule Properties, enter a rule name and click Edit Query Statement
- On the Query Statement Properties, click Show Query Language and copy paste below WQL code
[su_box title=”Warning” style=”glass” box_color=”#dac6c6″ title_color=”#F0F0F0″]select * from SMS_R_System where SMS_R_System.ClientType = 3[/su_box]
- Click Ok and Ok
- You’ll return to Membership Rules tab, click Next
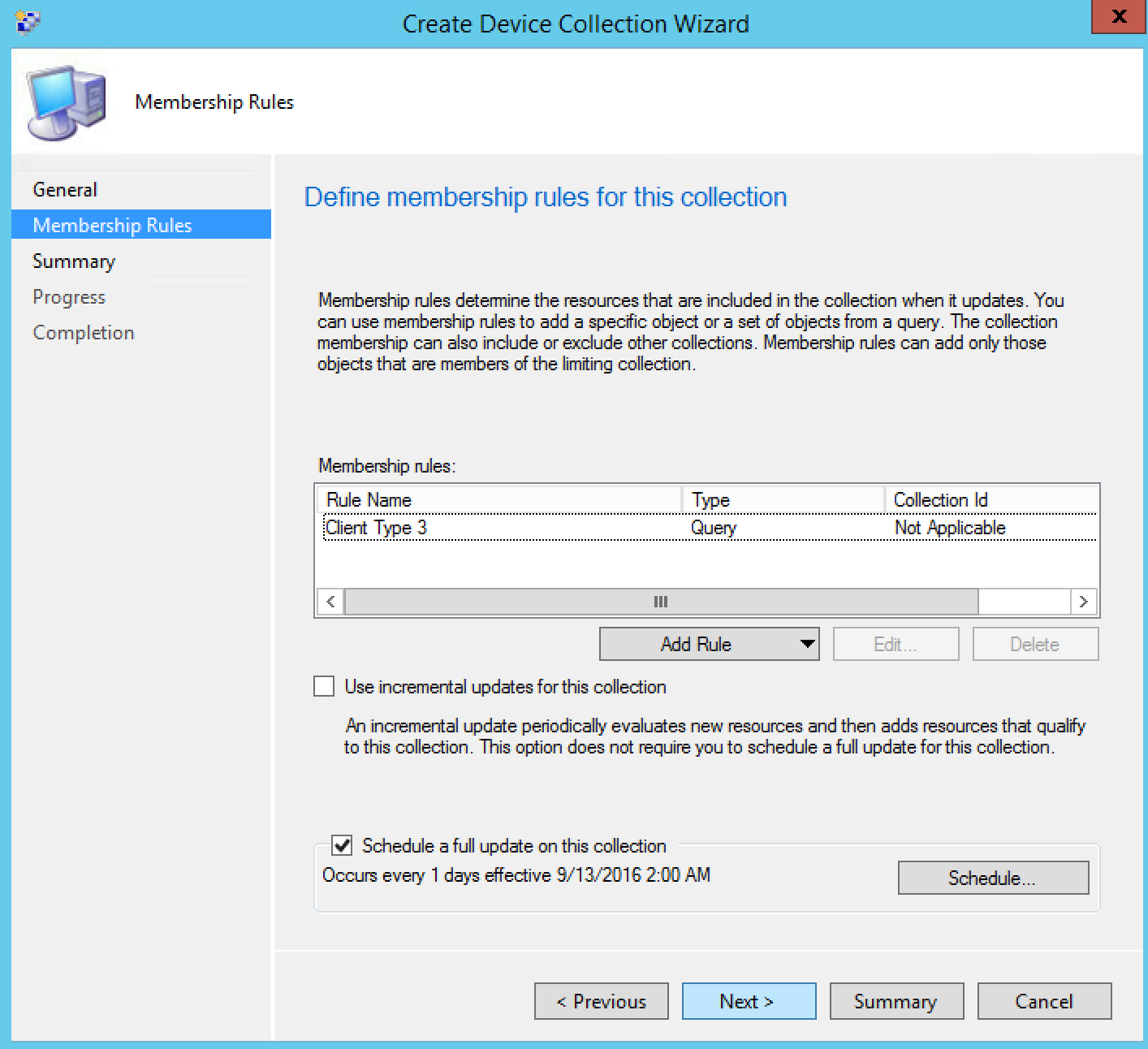
- Click Next and Close
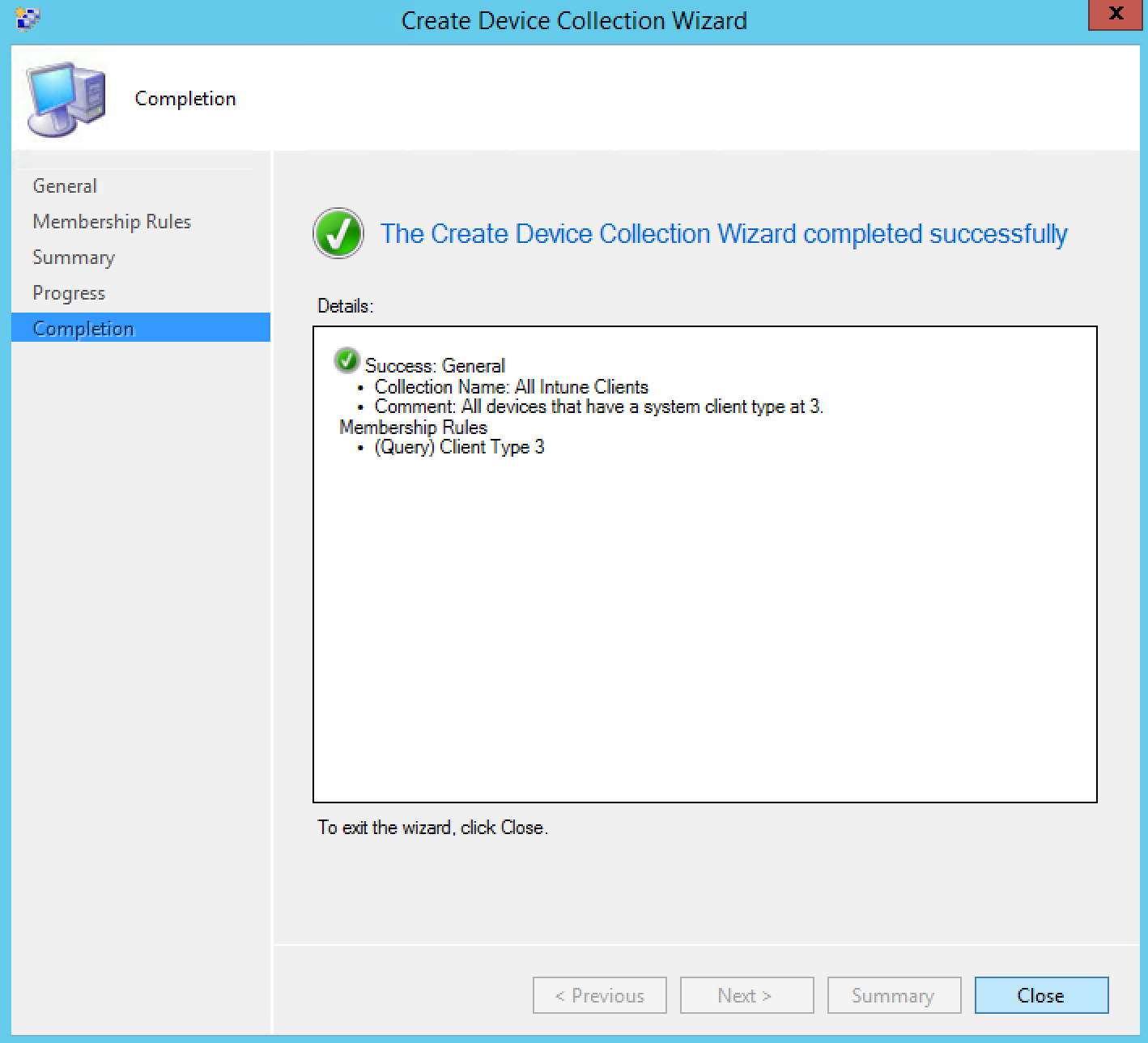
[su_note note_color=”#ff8787″ radius=”8″]This collection will be the main collection for the admins that work only with Intune devices in your SCCM console.[/su_note]
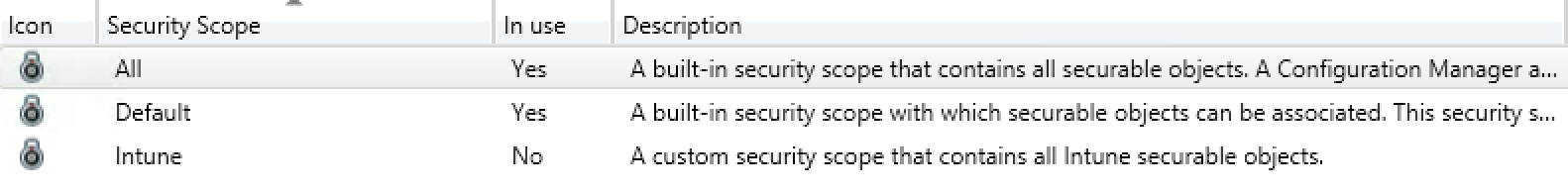
Create Security Scope to enhance SCCM Intune Security
Now that we can gather Intune devices in the console, we will create a security scope in order to assign this scope to all objects Intune. When we talk about objects in SCCM, we’re talking about configuration items, compliance policy, email profile, wifi profile, applications and many more.
- Open the SCCM console and navigate to Administration / Security
- Right-click on Security Scopes and select Create Security Scope
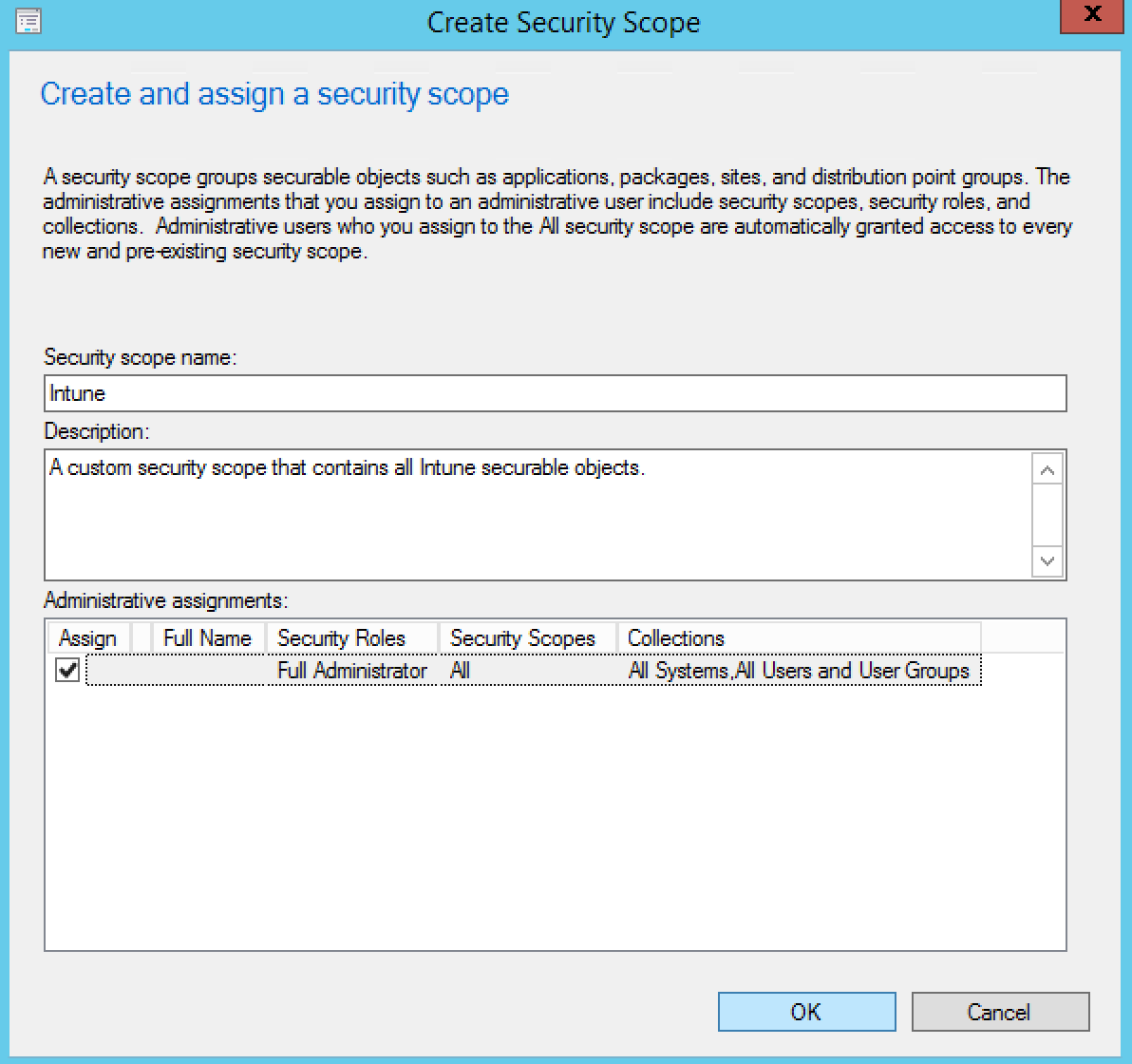
- On the Create and assign a security scope window, enter a name for your security scope like Intune
- By default, full admins have access to manage all security scope but you can add more admin groups if needed
- When done, click Ok
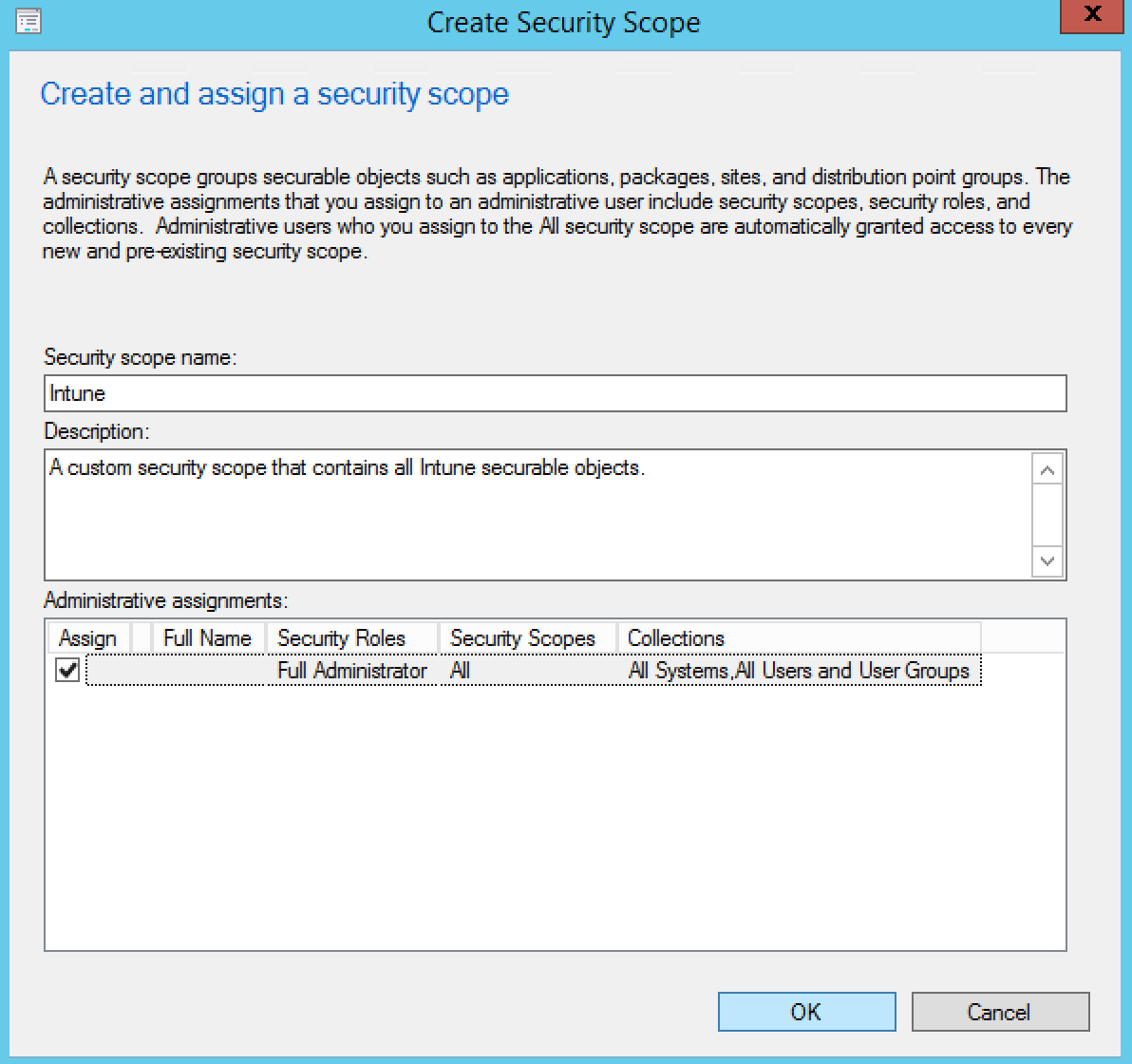
The security scope created for Intune is created :
Assign Security Scope to Intune Objects
Since we can now assign this new security scope, it is now time to assign it to all Intune objects. For example, an application that you deploy only for Intune clients versus applications that you deploy on Configuration Manager clients.
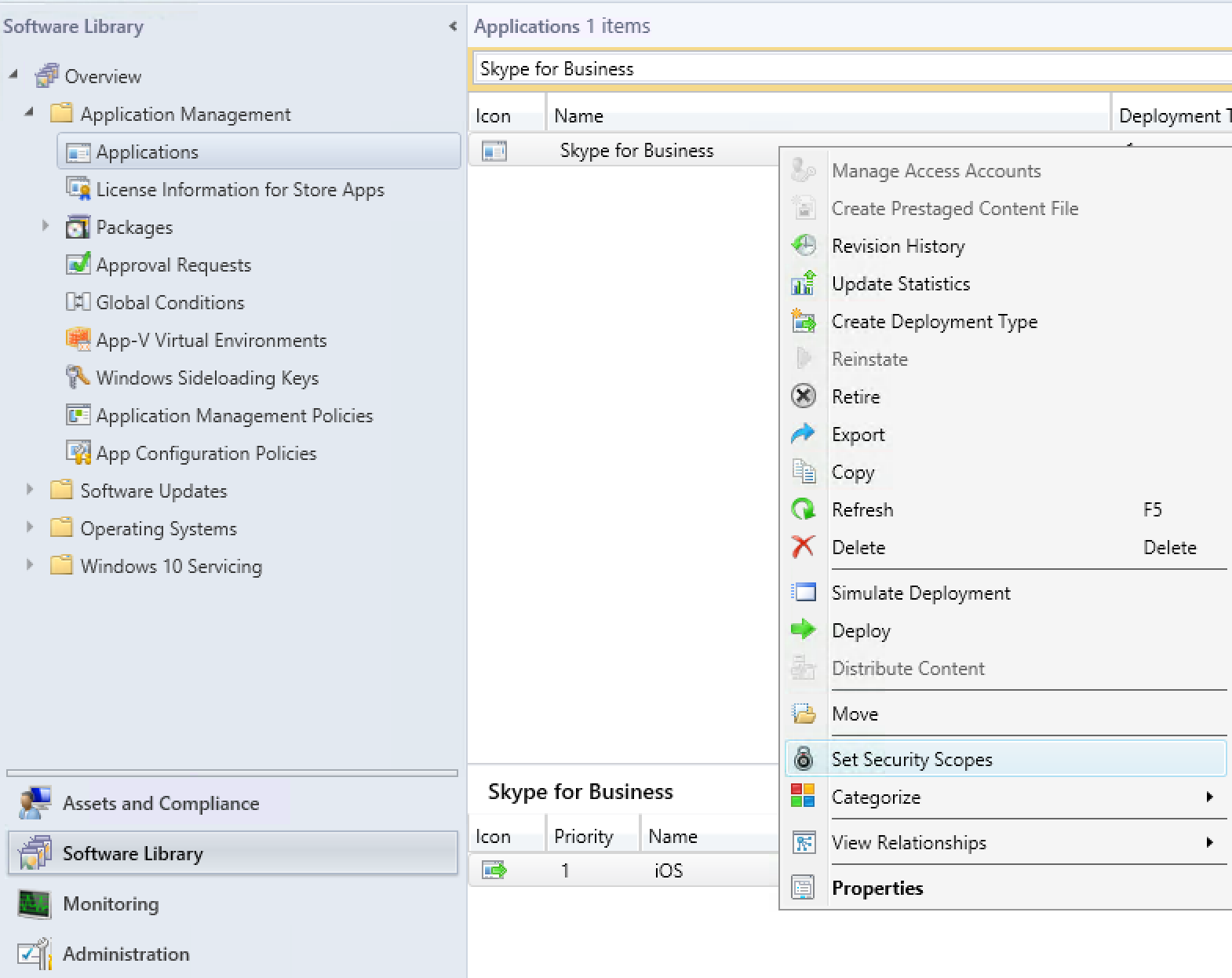
- Open the SCCM console and navigate to Software Library / Application Management / Applications
- Right-click on one or multiple Intune applications and select Set Security Scopes
- Remove check marks on all security scopes and add a check mark on Intune security scope
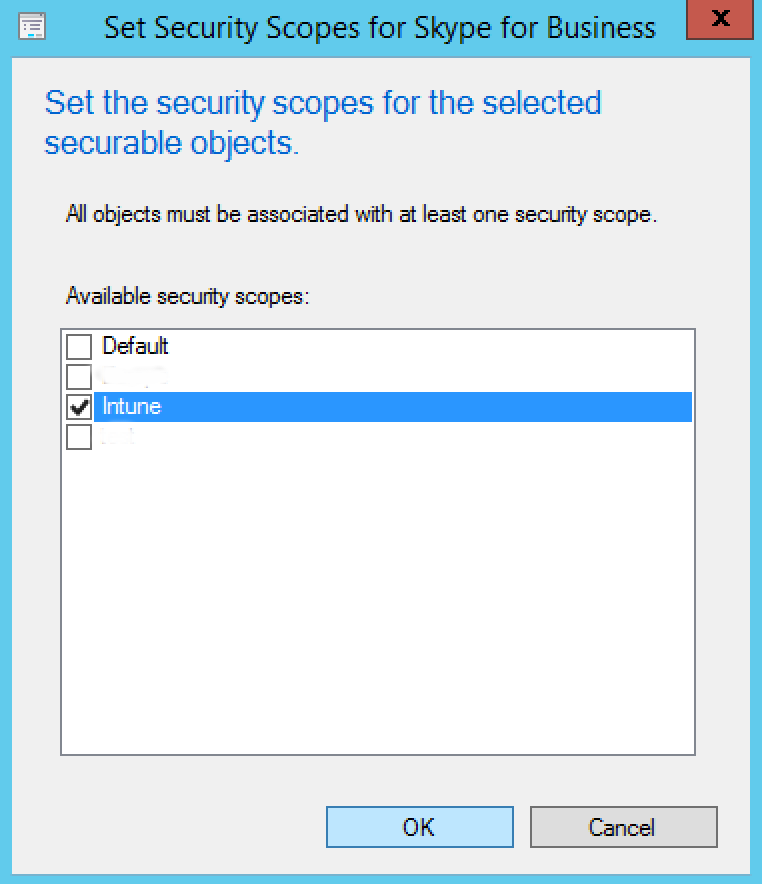
[su_note note_color=”#f0f0f0″ radius=”8″]Take note that Full Admins have access to look at all objects, even if default settings is unchecked. All other security roles must be assign to this security scope to see Intune objects in the SCCM console. By removing Default security scope, you make sure “non-admin” security role won’t see Intune objects and vice versa. [/su_note]
Repeat this section until all your Intune objects are tagged.
Create and Configure Security Role
The security roles were implemented in SCCM 2012 to add granularity in security with the SCCM console. This avoids giving full access to administrators who do not really have the knowledge to change certain configurations. Use it to minimize impacts and bad manipulations in the console. If you don’t understand the concept of security roles and security objects in SCCM, we suggested that you read this Technet post.
- To create a security role, open the SCCM console and navigate to Administration / Security
- Right-click on a security role you want to copy (in our example we select Asset Manager) and select Copy
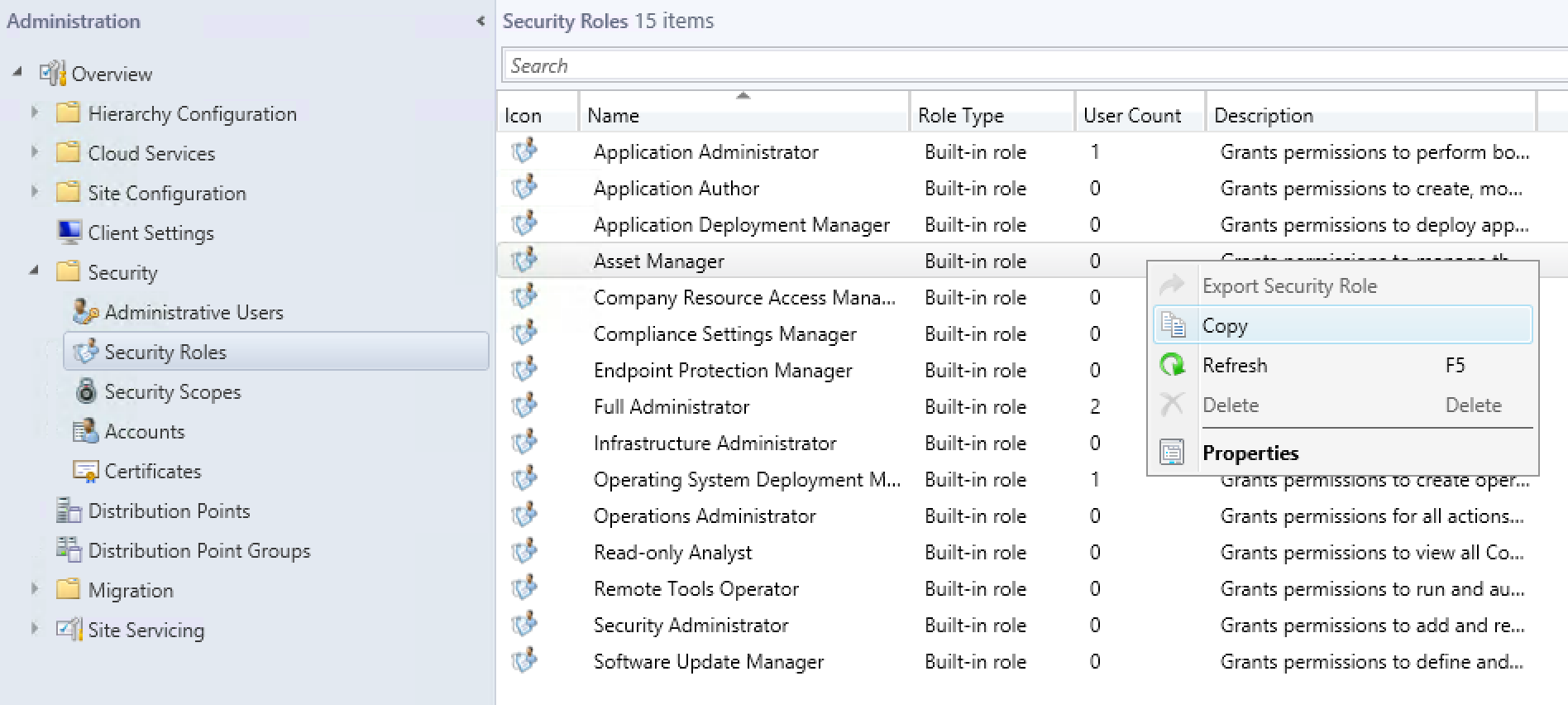
- At the Copy Security Role window, enter a role name, and once you’ve configured your permissions, click Ok
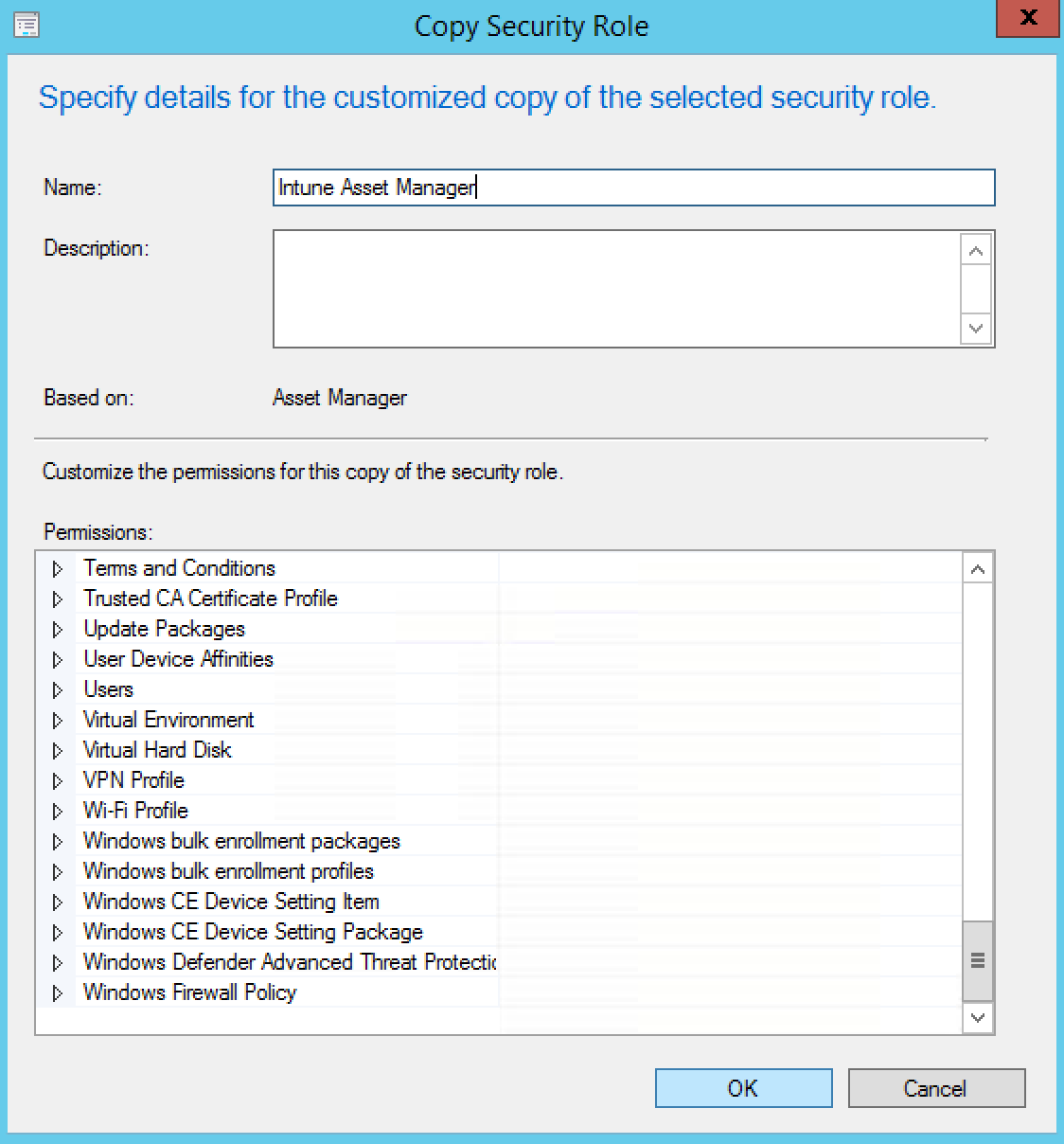
- You have now created your custom role for Intune
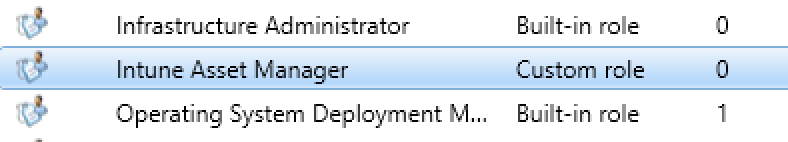
Create and Assign Administrative Users or Groups to the Intune Security Role
The final step is to assign all these configurations you’ve made, to an administrative users or groups. It’s best to use security groups in Active Directory for security management because it’s easier to manage, instead of constantly manage individual access in SCCM console. This section is the most important part because it’s the time to stick together all these configurations.
- Open the SCCM console and navigate to Administration / Security / Administrative Users
- Right-click on Administrative Users and select Add User or Group
- At the Add User or Group windows, choose the security group you create in Active Directory by clicking Browse
- Click Add and choose the security role you created at the section 4, in our case it was Intune Asset Manager
- At the Assigned security scopes and collections section, remove all default instance
- Click on Add, select only the All Intune Clients and the security scope Intune as shown below
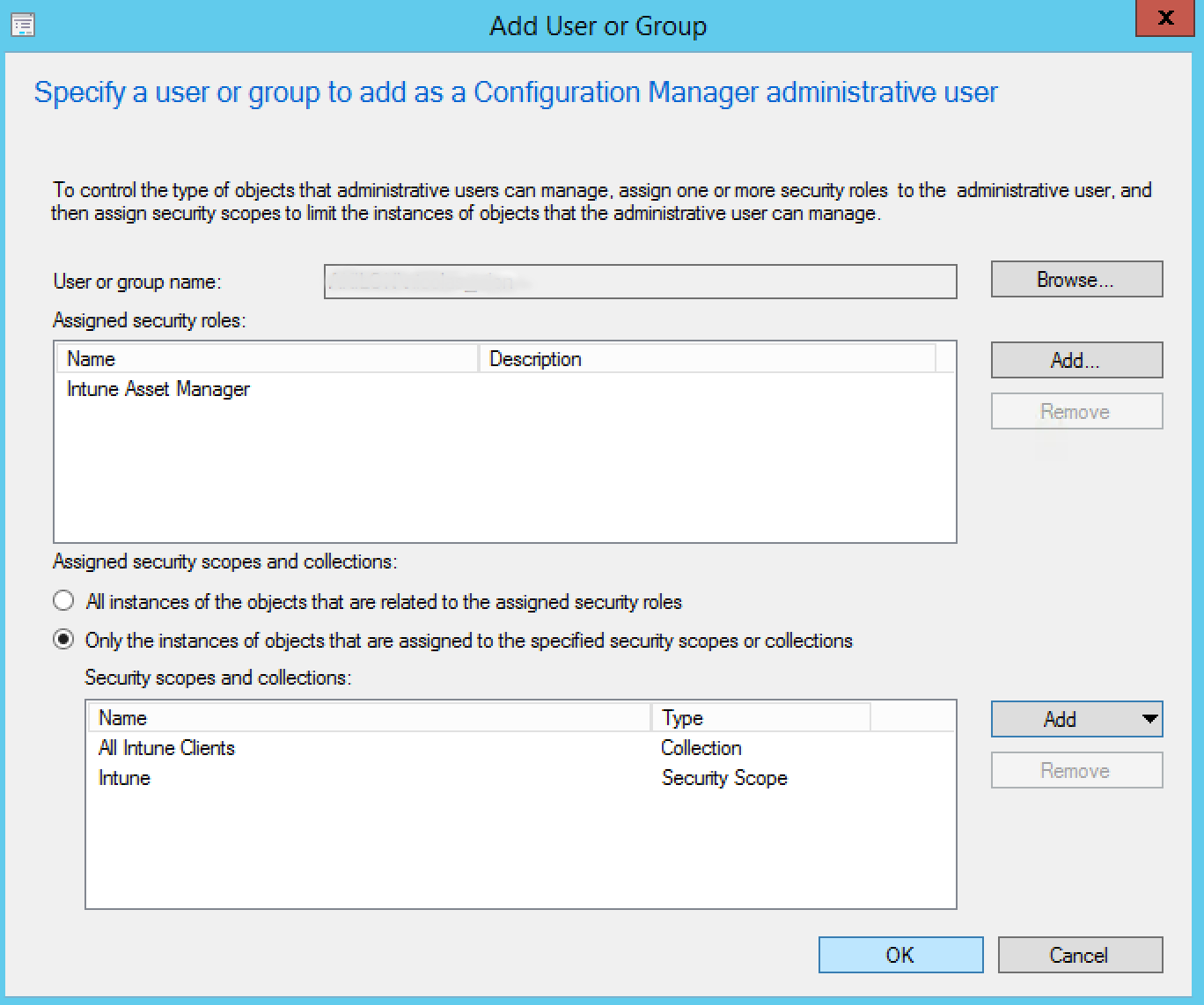
- Click Ok when you’re done
Summary
Finally, we suggest that you test your configuration by adding a test user in your Active Directory security group. Log into the SCCM console and only the Intune mobile devices and objects should be visible. Additionally, the SCCM access delegation with RBAC is very useful in some situations and can help you avoid fatal errors.
How do you manage access in the SCCM console for you Intune Devices ?












Only authorized users can leave comments
Log In